ecosystem-guides.com
....exploring the planet's ecosystems
INDO-MALAYAN
Lowland Tropical Rainforest
Rainforest is the dominating natural vegetation type in much of tropical Asia, especially before humans began to develop the region. It ranges over a huge area; from Bali, then west through Java, Sumatra, north into Borneo, peninsula Malaysia, Thailand, the Philippines and up into southern China, then west into India and Sri Lanka.
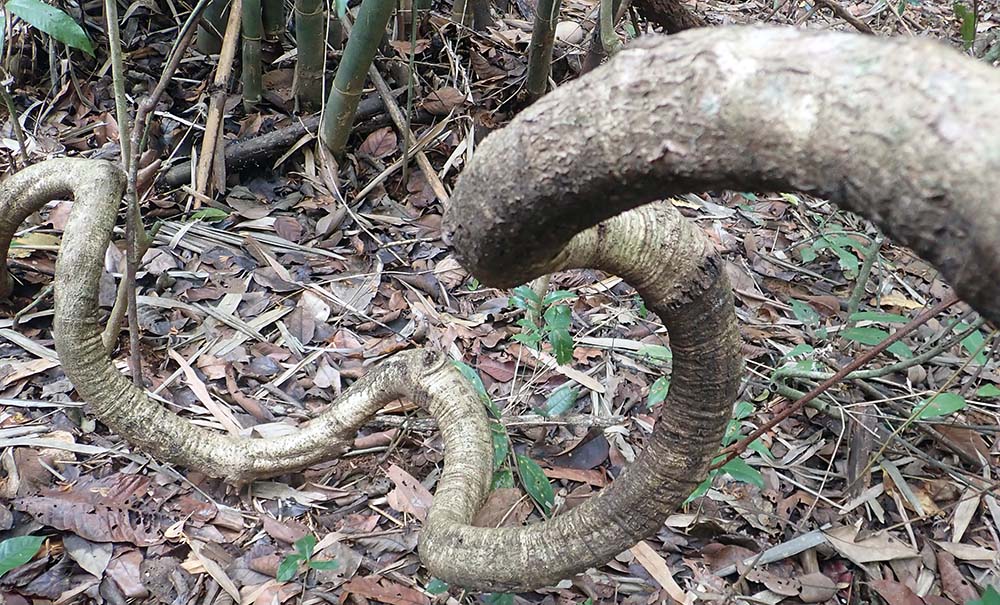 Large woody vines known as lianas, are common in the rainforest., (Jahoo, Cambodia).
Large woody vines known as lianas, are common in the rainforest., (Jahoo, Cambodia).Within that large zone it obviously varies in plant and animal composition, particularly with much of the land being separated by ocean in our current interglacial time. Additionally, within that moist forest, there is variation in altitude, which results in many vegetation communities: from steamy lowland jungle on the coast, to cooler subtropical rainforest in the highlands and stunted cloud forest in the mountains.
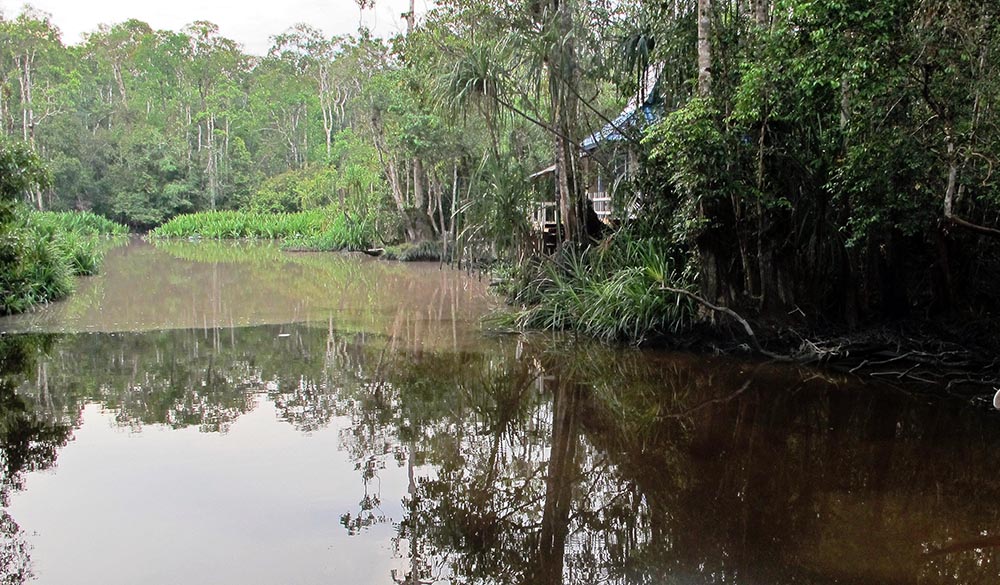 A small clearer tannin-stained black water creek meets a larger murkier brown water river in Indonesian Borneo.
A small clearer tannin-stained black water creek meets a larger murkier brown water river in Indonesian Borneo.These wet tropical rainforests are host to many 'plant-like' organisms...
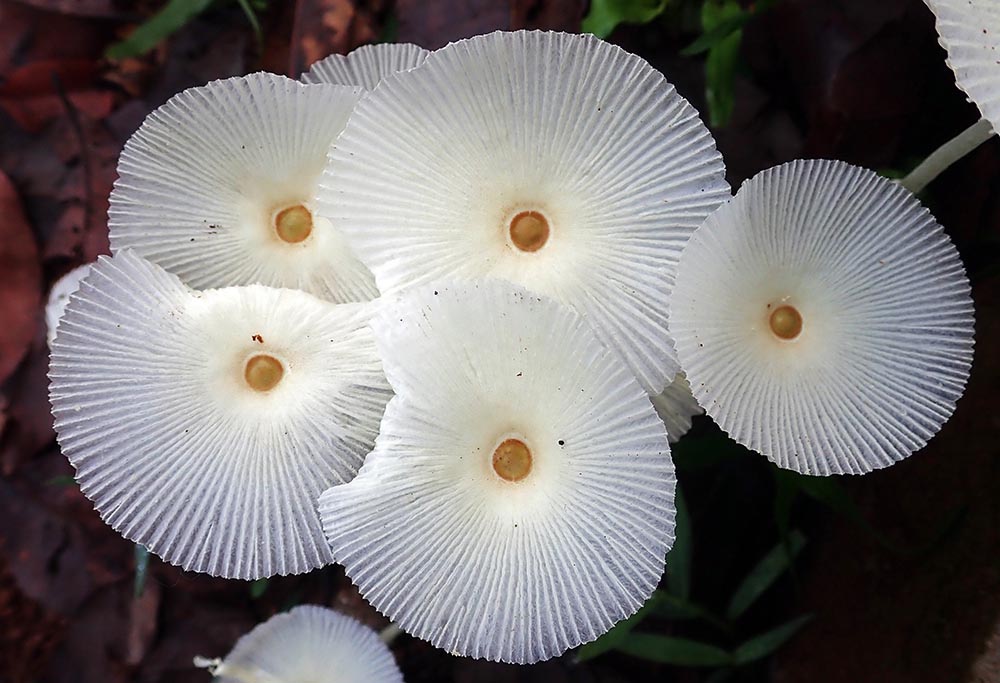 Fungi
Fungi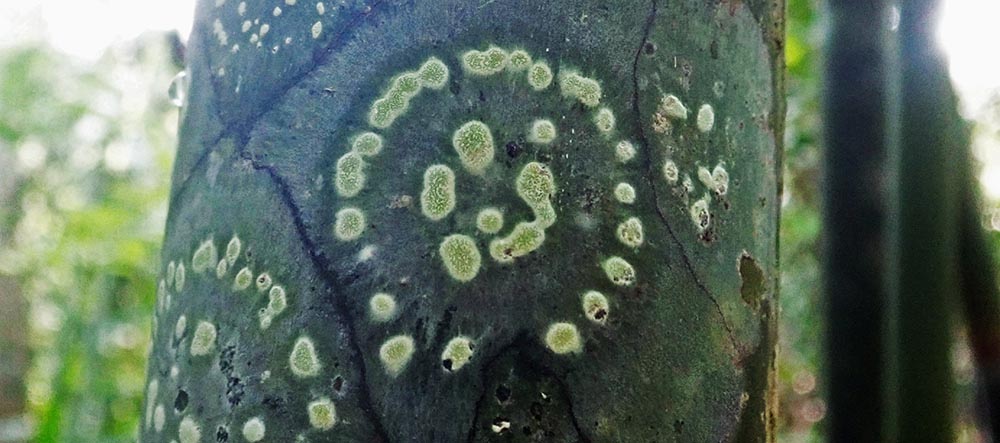 Lichen
LichenThere are some 1,200 species in the family Clusiaceae, and they are found throughout the tropics of the world. The trees in this family often have very smooth, glossy leaves with fine venation that is almost perpendicular to the main central vein. They often have yellow latex when the leaves are torn.
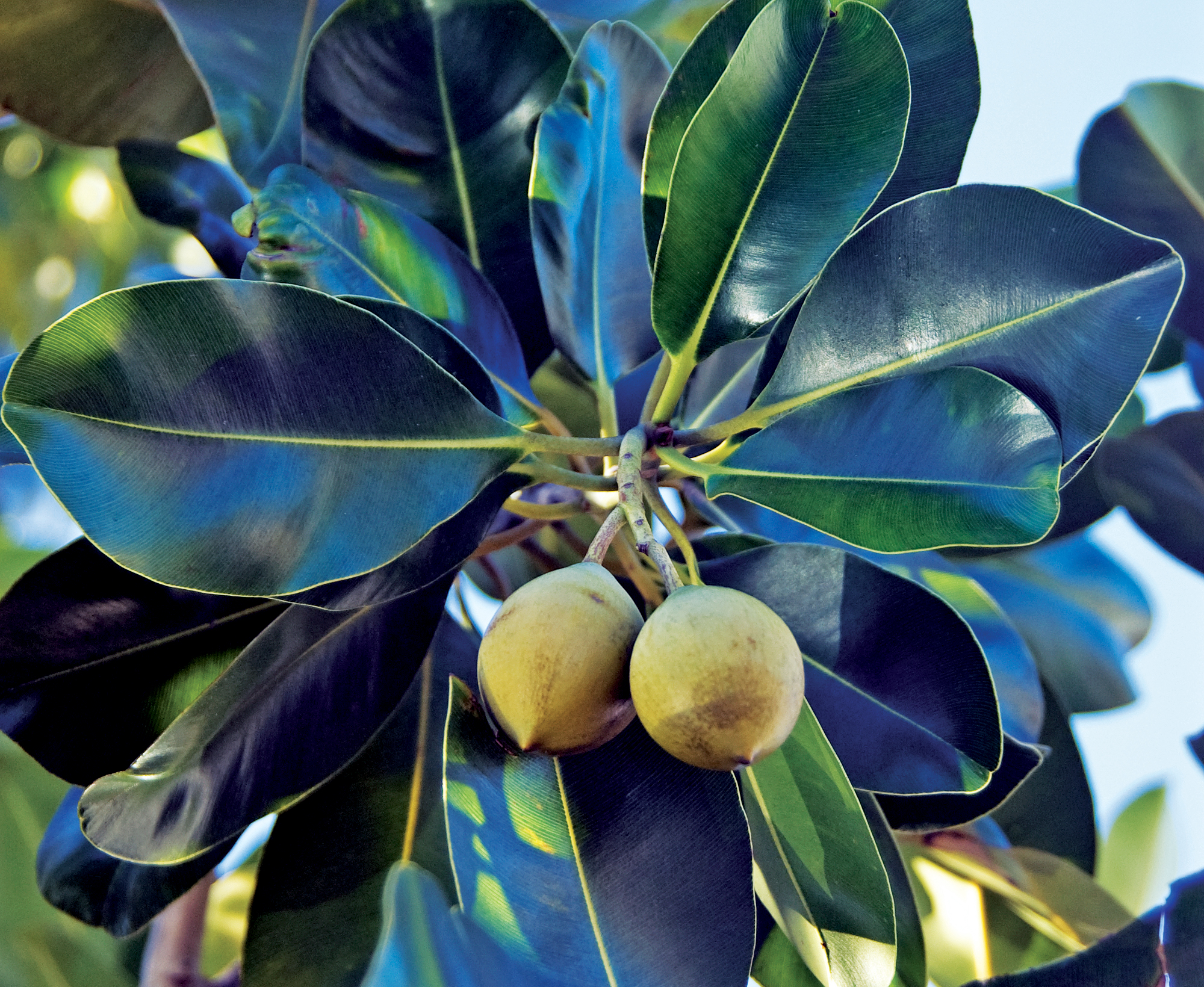
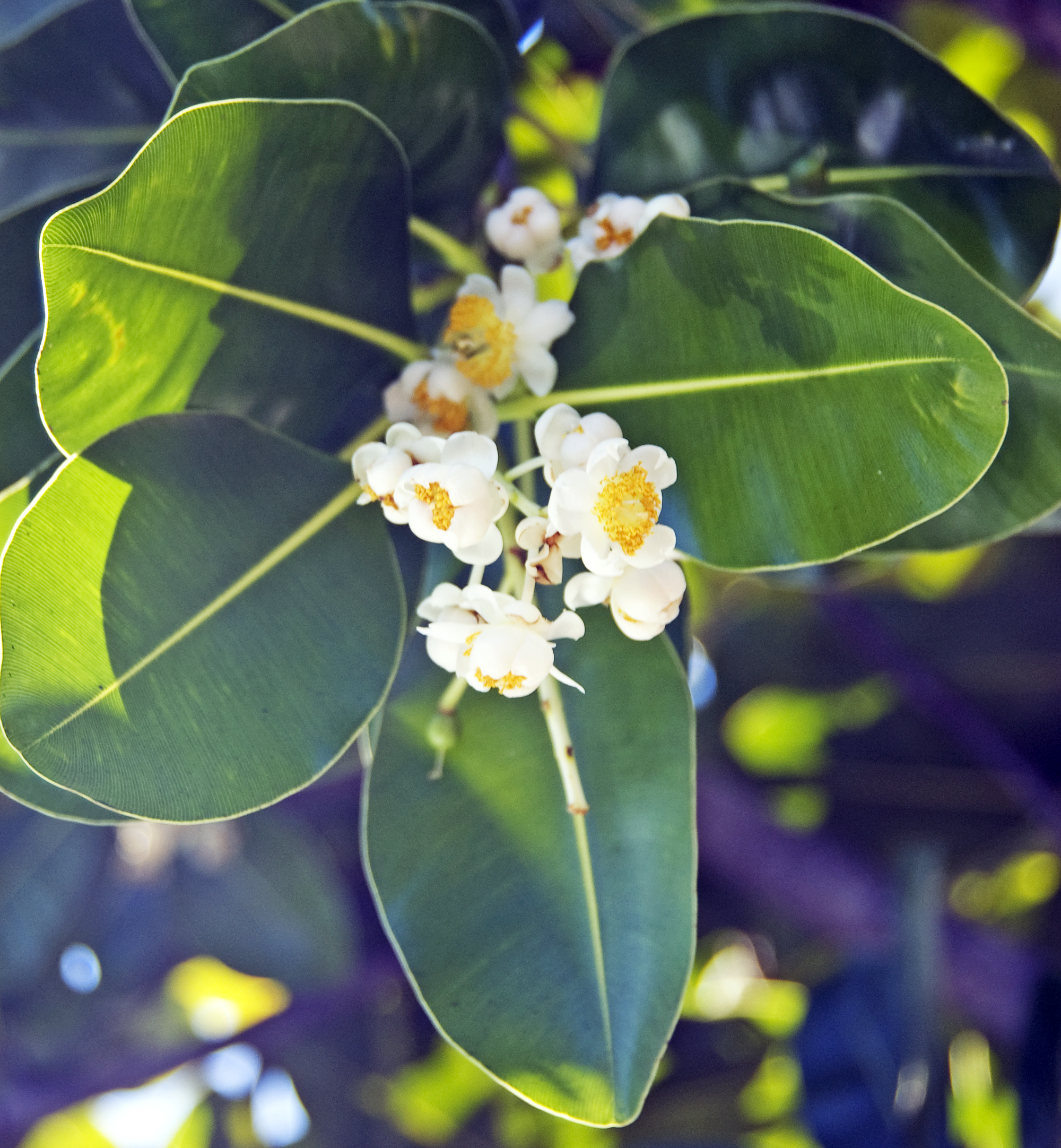
There are over 180 species in the genus Calophyllum and they are found throughout the tropics of the world. The scientific name translates to "Beauty Leaf”. A common and dominant species in rainforest along the coast in tropical Asia is Calophyllum inophyllum. It can grow quite large, the scaly trunk growing from coastal forest, then leaning over the sandy beach. The leaves very smooth and glossy with fine, close venation, the flowers are white and yellow, and are followed by round green fruits that end up on beach.


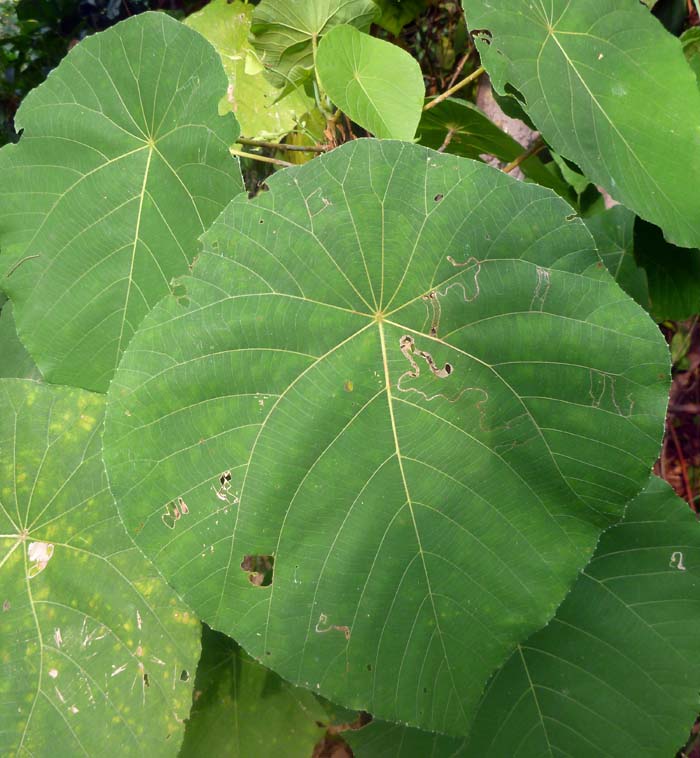
The genus Macaranga incudes species that are among the most common of tropical Asian jungle plants, as they are pioneer species: those that grow fast and quick on the edge of the rainforest.
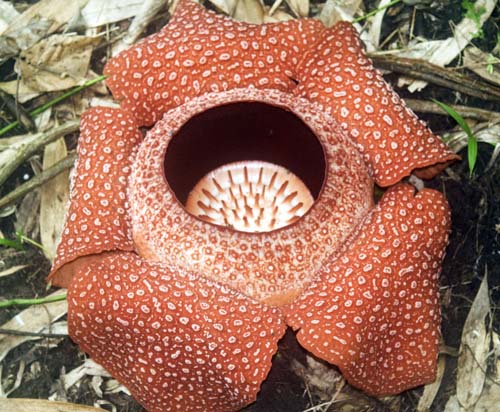
 (Krakatoa, Indonesia)
(Krakatoa, Indonesia)The family Rafflesiaceae contains the biggest flowers in the world. They are only found in the rainforest of south-east Asia. Contrary to popular belief, they don't stink; (that's another large tropical flower called Amorphophallus titanum).

The family Nepenthaceae contains the tropical Asian Pitcher Plants. These are carnivorous plants.
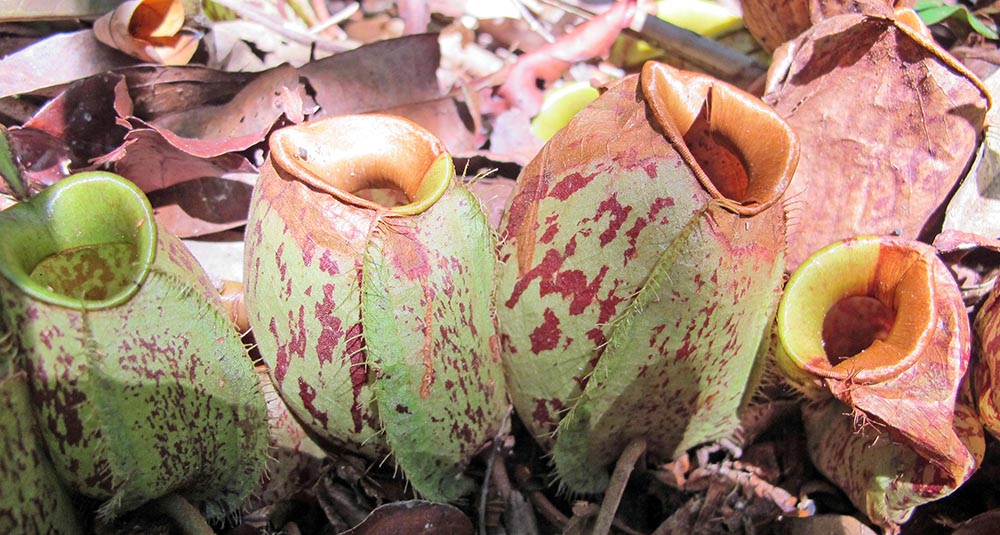 (Tanjung Puting National Park, Borneo, Indonesia)
(Tanjung Puting National Park, Borneo, Indonesia)Millipedes and Centipedes are long with many legs. Millipedes are generally slower, and feed on decaying vegetation. Centipedes can be much faster, and often predate on other invertebrates. The latter can have painful bites, while the former have chemical defences. Millipedes tend to roll into a defensive ball when touched; centipedes shouldn't be touched!
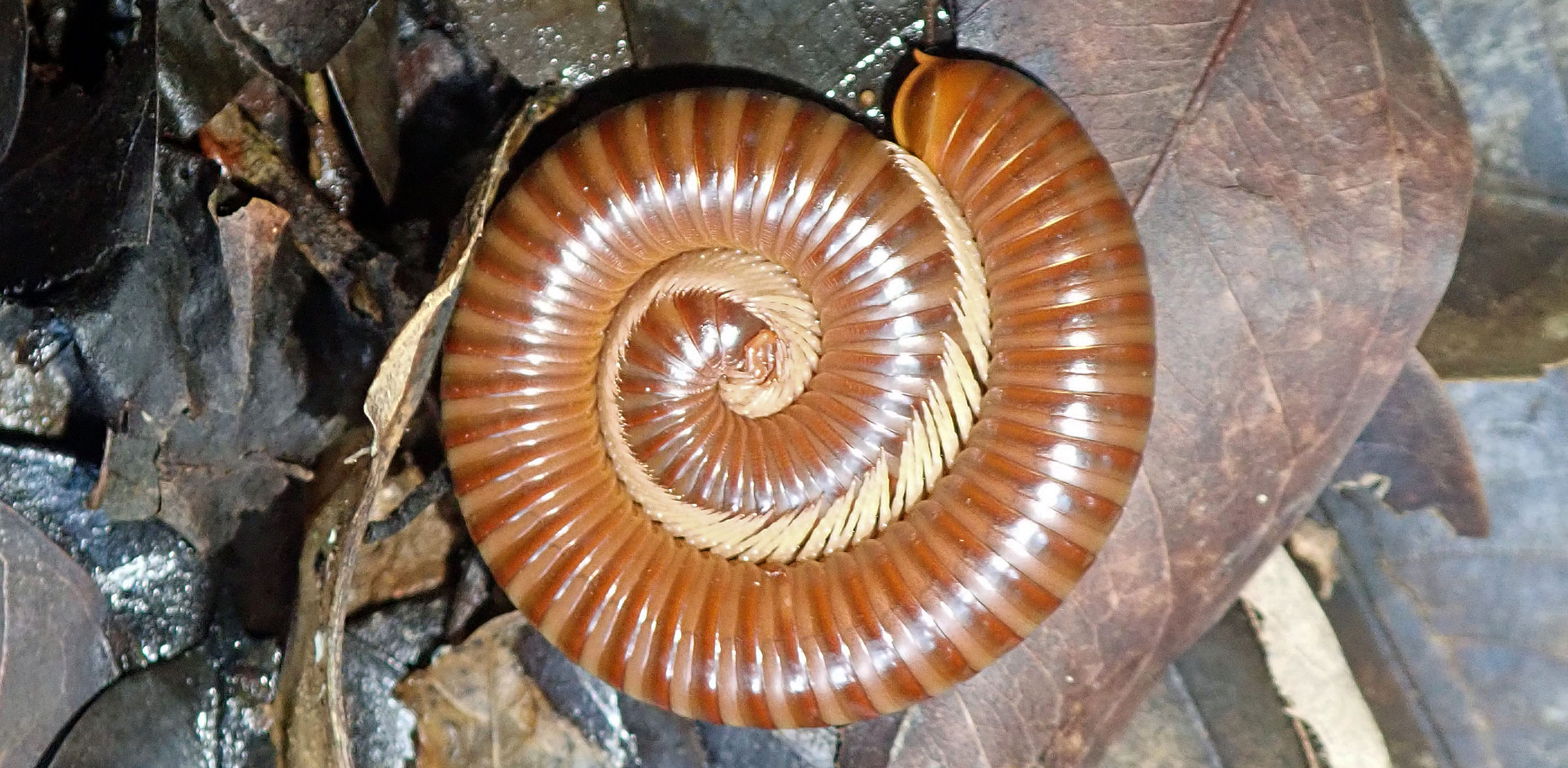 Millipede, rolled up in defence (Cambodia)
Millipede, rolled up in defence (Cambodia)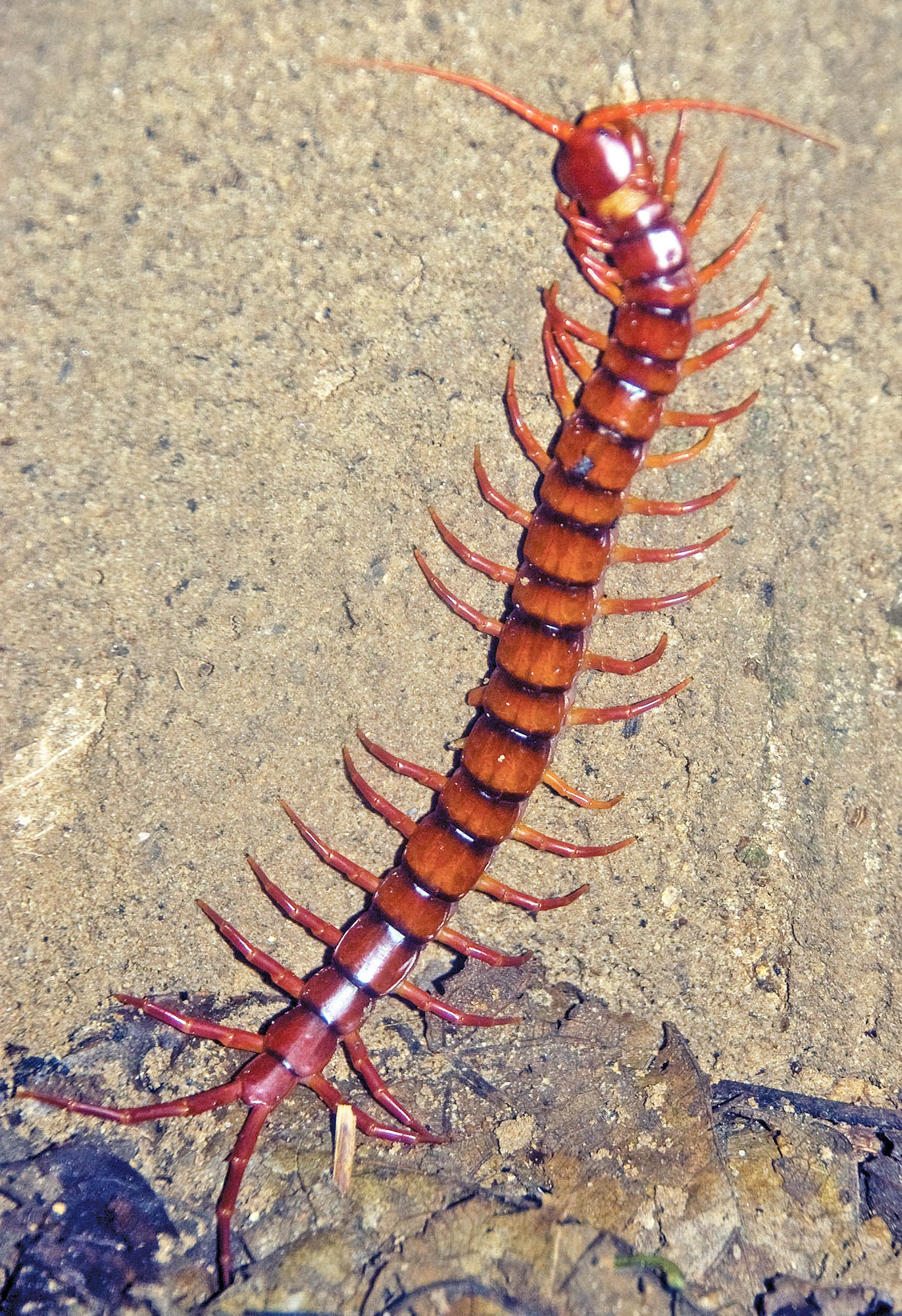 Centipede (Taman Negara, Malaysia).
Centipede (Taman Negara, Malaysia).Arachnids include spiders, scorpions, whip scorpions, harvestmen and other eight legged creatures. The 'Harvestmen' of the order Opiliones are delicate creatures that are not often noticed, but are quite common on the floor of the Asian rainforest.
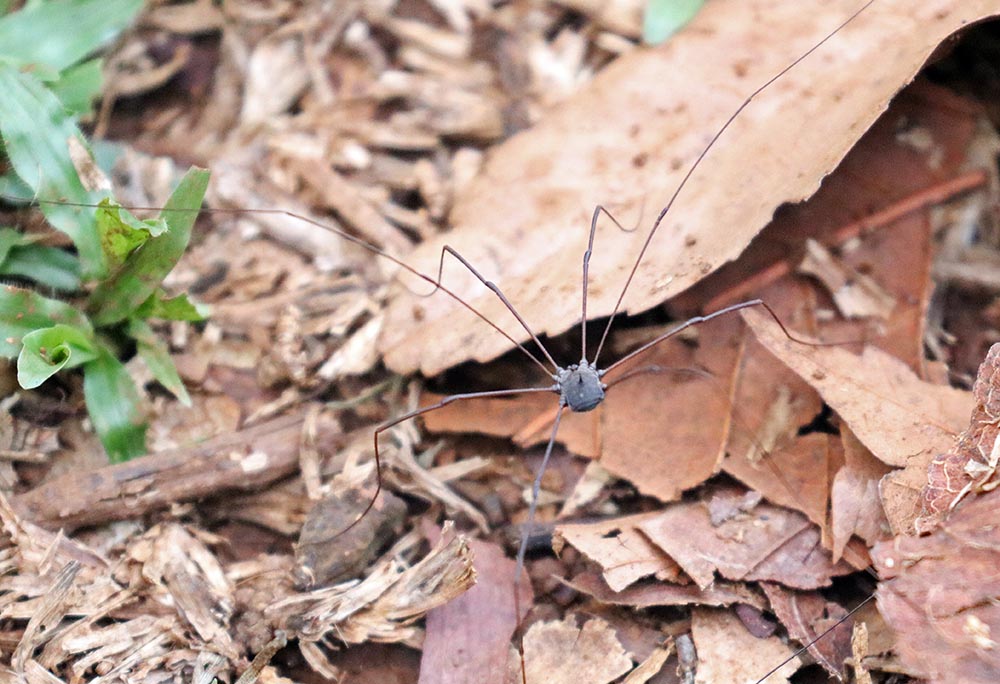 (Nature Lodge, Sen Monoron, Cambodia)
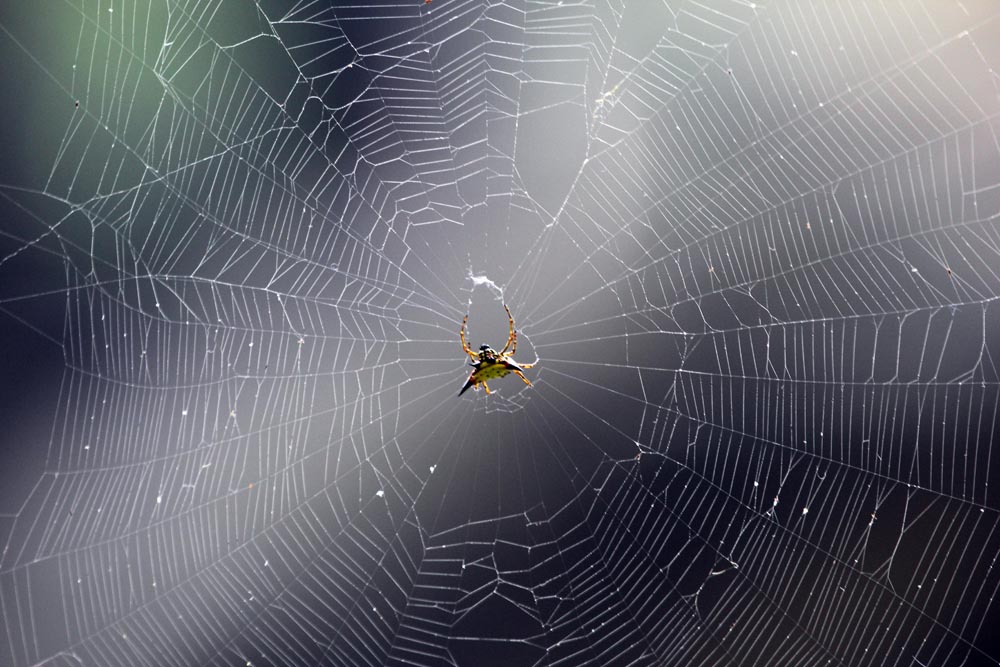
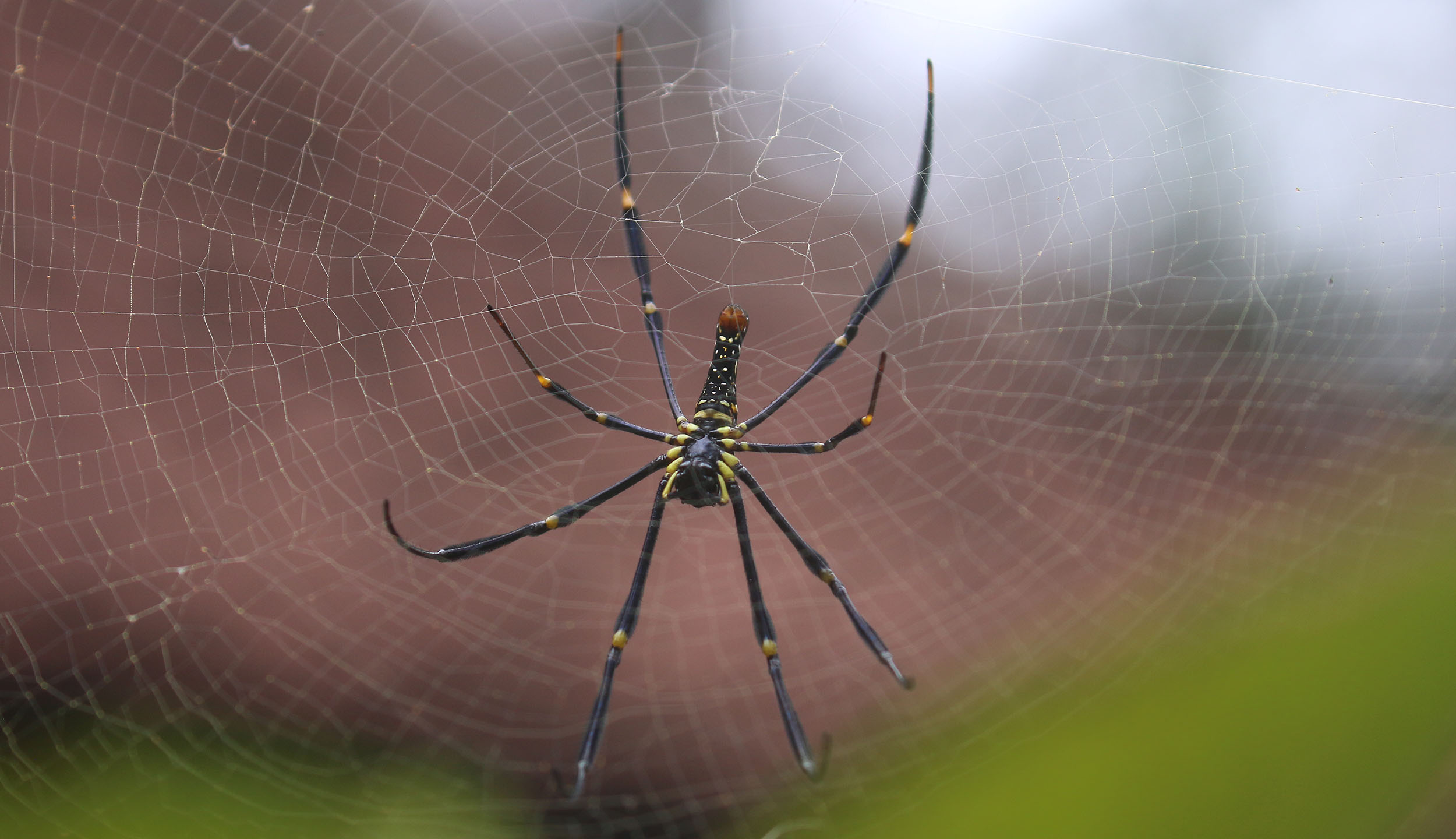
(Nature Lodge, Sen Monoron, Cambodia)The true spiders vary in size in the Asian jungle. The 'Spiny-back Spiders' are small but usually colourful spiders with variously shaped ornate spines. They are not dangerous. The highest diversity of these spiders is in tropical Asia. At the other end of the size scale are the Nephila, the 'Golden Orb-Web Weavers' are the largest spiders seen in a web on the planet. It is the female that is the large spider in the middle of the web; the males are tiny.


The order Thelyphonida includes the rarely seen 'Whip Scorpions'.
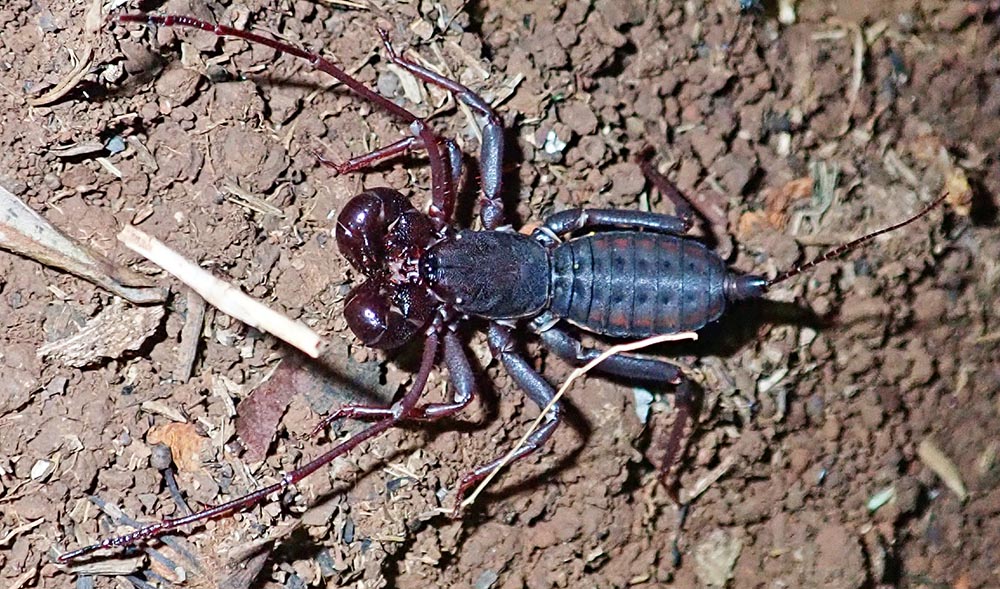 (Jahoo Gibbon Camp, Cambodia)
(Jahoo Gibbon Camp, Cambodia)The insects are incredibly diverse in the lowland rainforests of tropical Asia.
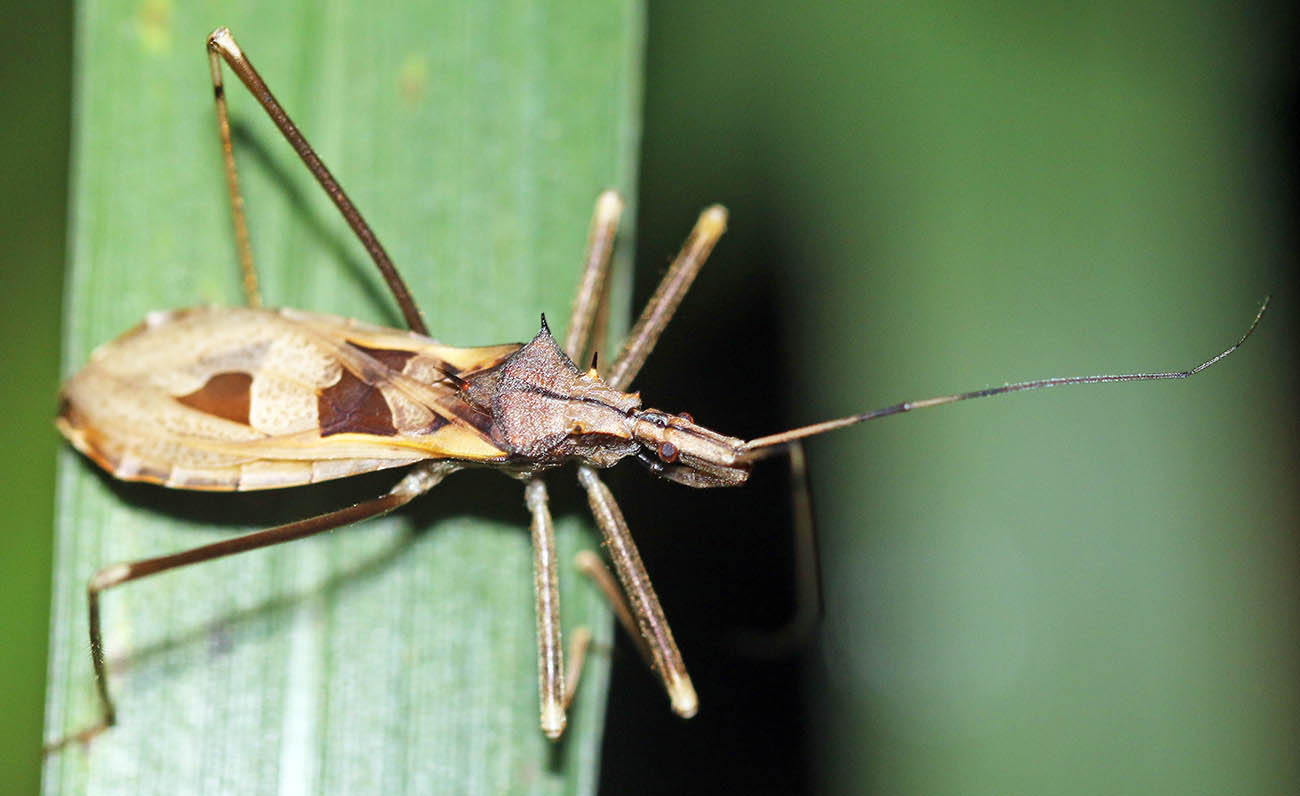 (Subic Bay, Philippines)
(Subic Bay, Philippines)Dragonflies (higher image below) usually land with their wings out a right angles to their body, in contrast to Damselflies (lower image below), that hold them back along their body. They look a little scary, but they are harmless (to humans, but not to the tiny insects that they catch and eat)
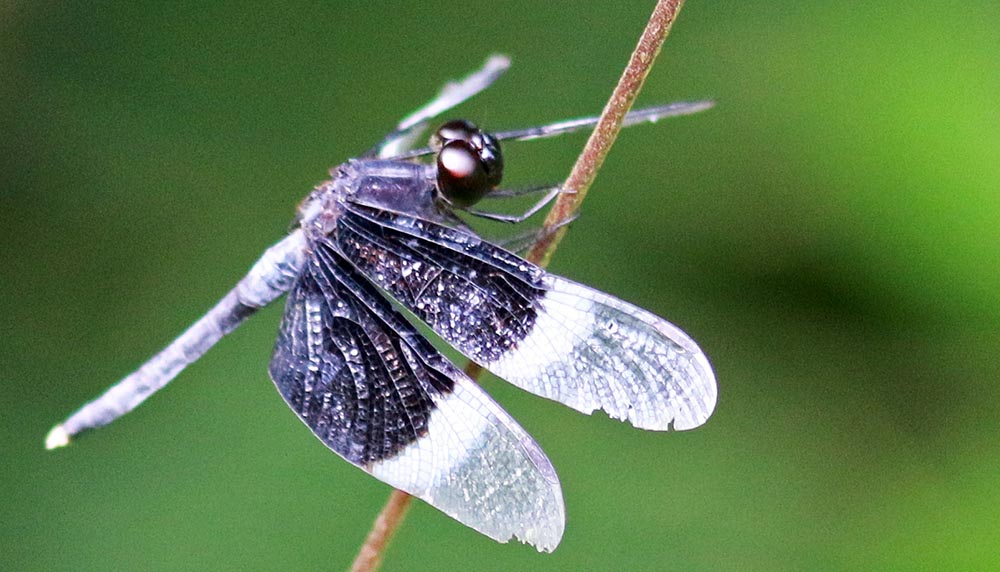
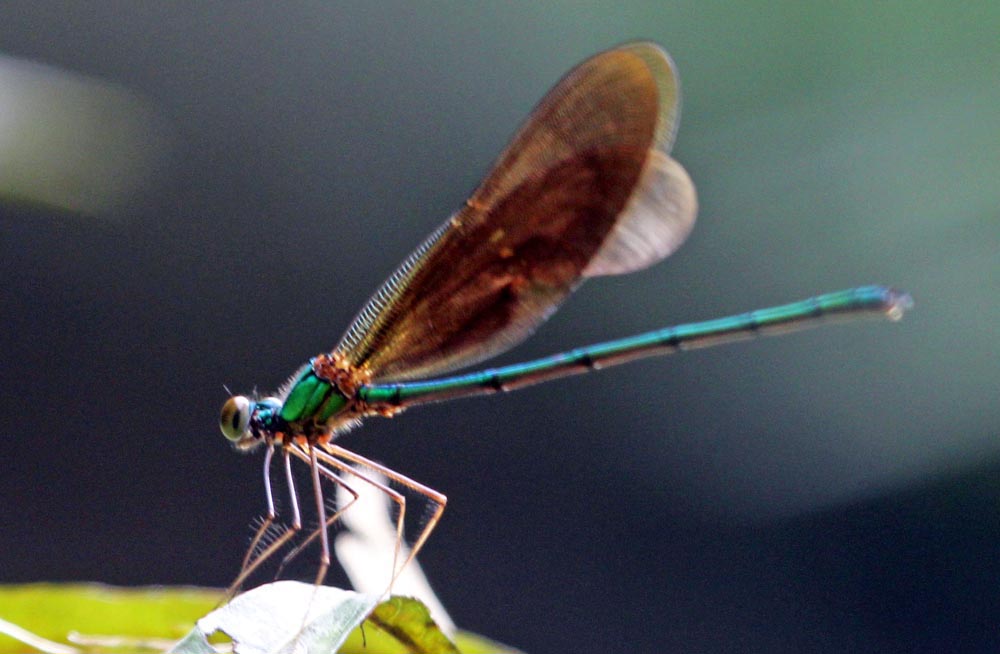


Termites of the order Isoptera may be seen crawling along the moist ground of the forest, especially at night.

There are some great species in the cricket and grasshopper order Orthoptera, including bright green Katydids. Below is (maybe) Despoina spinosa, a katydid that feeds on the foliage of figs.

Of course the biggest and most speciose group of anything are the Beetles, and in the south-east Asian jungle it is no different....
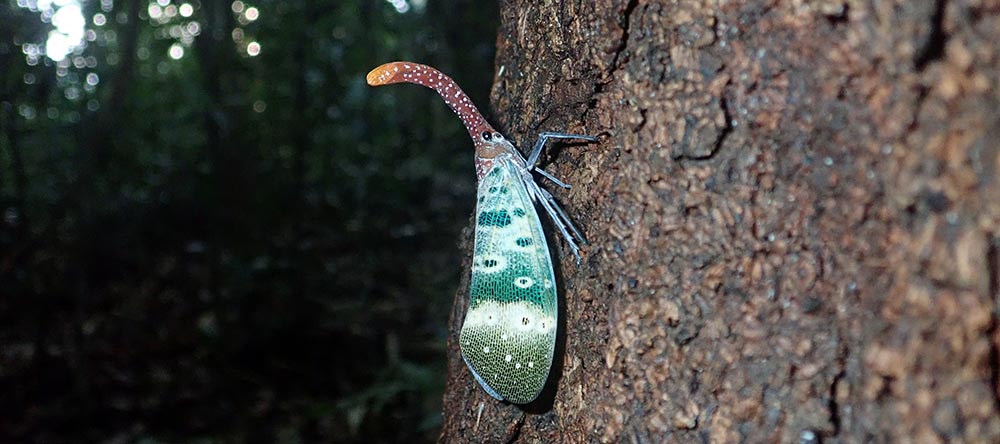 'Lantern Fly' (Jahoo Camp, Cambodia)
'Lantern Fly' (Jahoo Camp, Cambodia)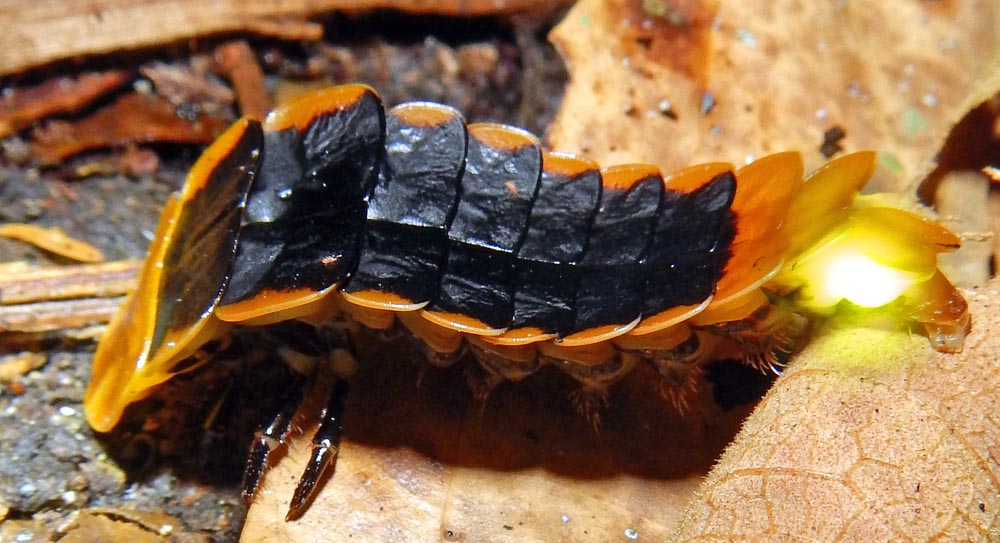 Firefly larvae. Not to be confused with Platerodrilus 'Trilobite Beetles' (Khao Yai, Thailand)
Firefly larvae. Not to be confused with Platerodrilus 'Trilobite Beetles' (Khao Yai, Thailand)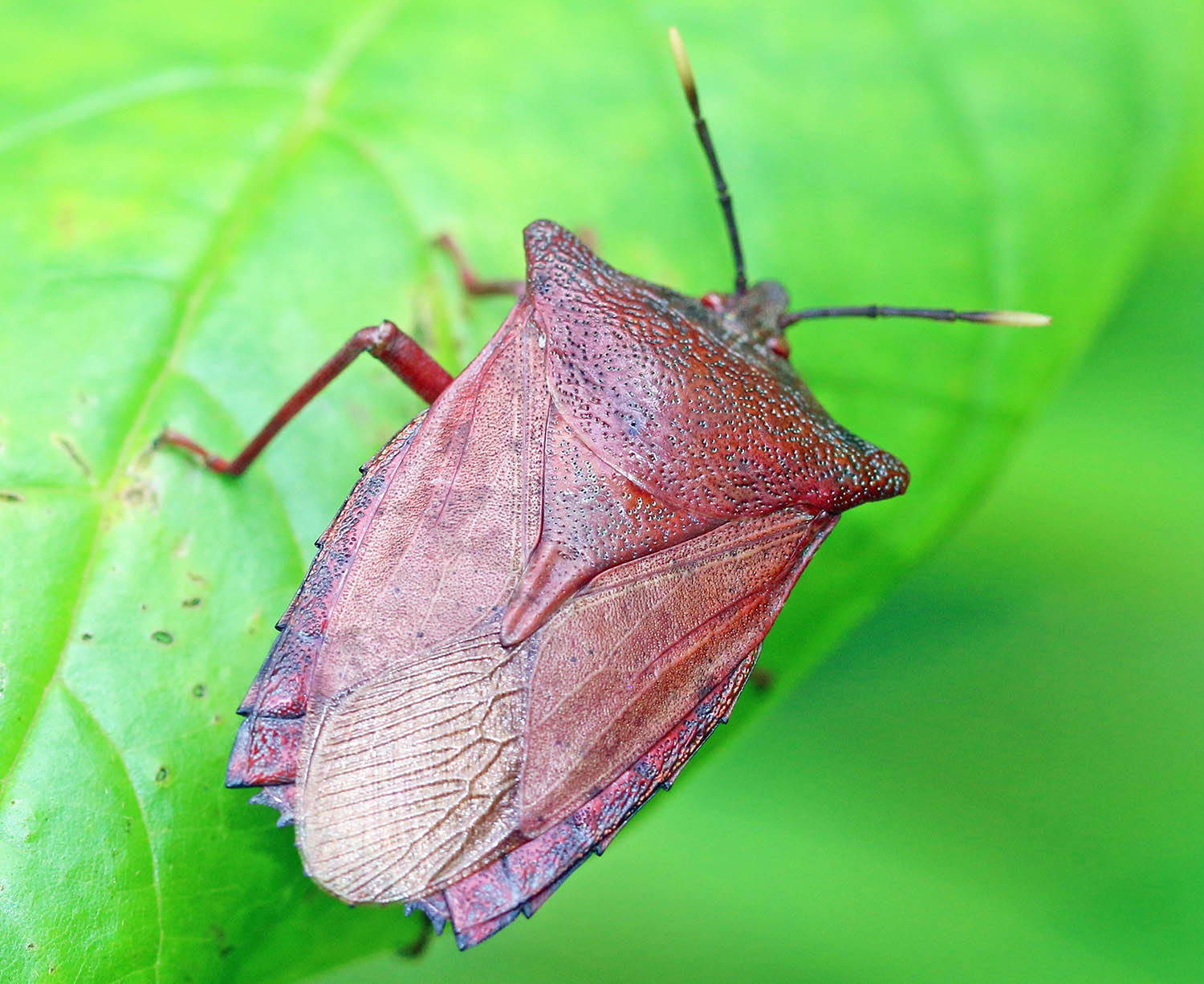 Stink/Shield Beetle (Subic Bay, Philippines)
Stink/Shield Beetle (Subic Bay, Philippines)You want to see a high diversity of butterflies and moths? Well you've come to the right habitat!
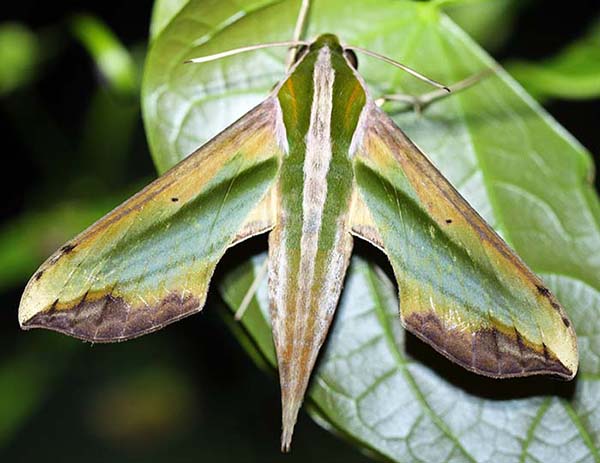 'Green Pergesa Hawk Moth' (Samarn Bird Camp, Thailand).
'Green Pergesa Hawk Moth' (Samarn Bird Camp, Thailand). 'Owl Moth' (Samarn Bird Camp, Thailand).
'Owl Moth' (Samarn Bird Camp, Thailand).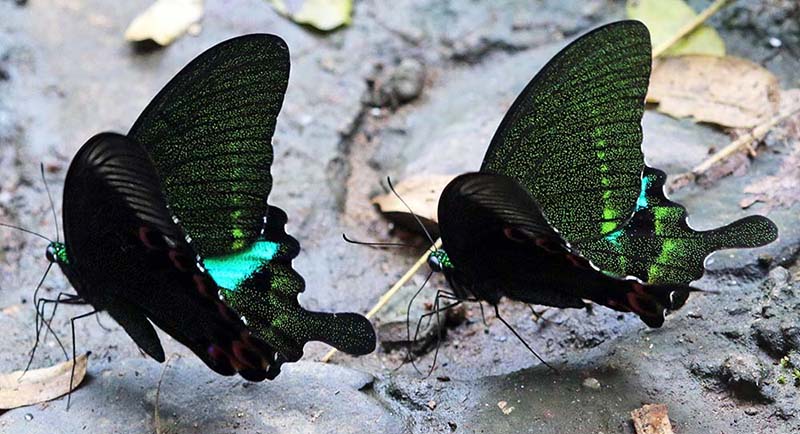 'Paris Peacock Butterfly' (Palau-U Waterfall, Thailand).
'Paris Peacock Butterfly' (Palau-U Waterfall, Thailand).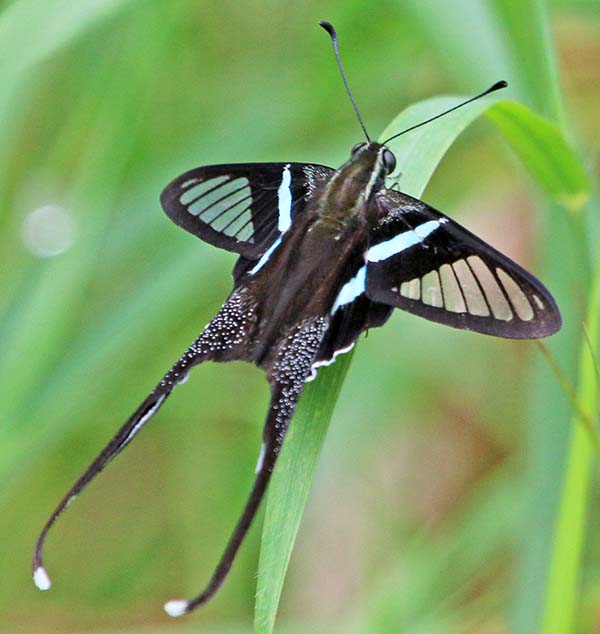 Lamproptera meges (Subic Bay, Philippines).
Lamproptera meges (Subic Bay, Philippines).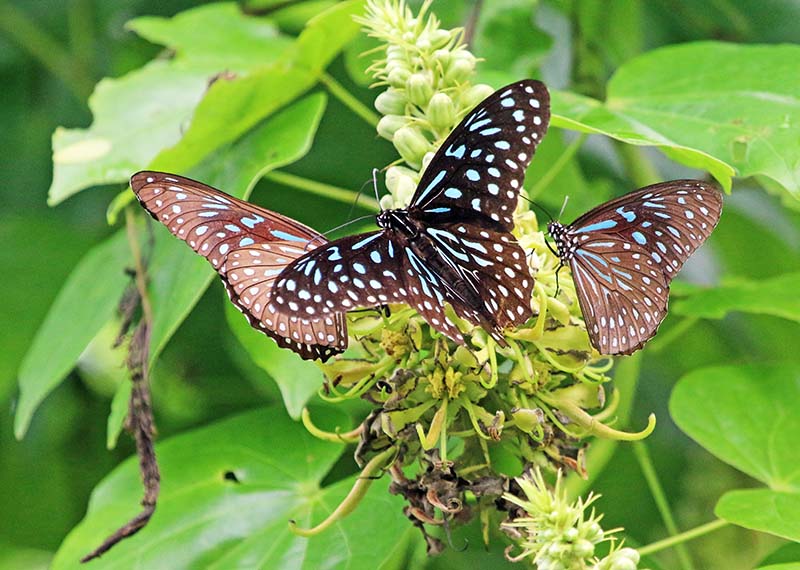 'Blue Glassy Tiger' (Kaeng Krachan National Park, Thailand).
'Blue Glassy Tiger' (Kaeng Krachan National Park, Thailand).Frogs love it hot and wet, and that's what they get in the jungle of tropical Asia...
 (Jahoo, Cambodia)
(Jahoo, Cambodia)One of the most distinctive groups of frogs in Asia are the 'Horned Frogs'. They are large amphibians, often with projections above the eyes that help them blend in with the leafy floor of the forest.
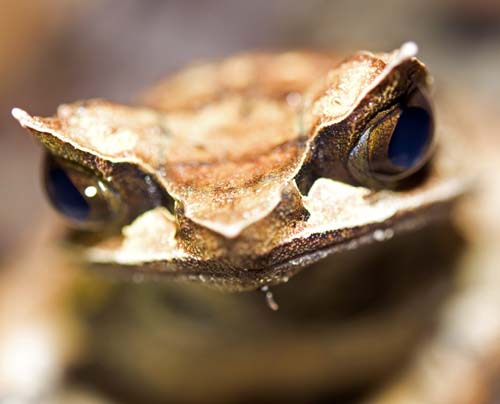 'Malaysian Horned Frog'
'Malaysian Horned Frog'Some of the biggest amphibians in the forest, and the more common ones in human settlements, are the toads.
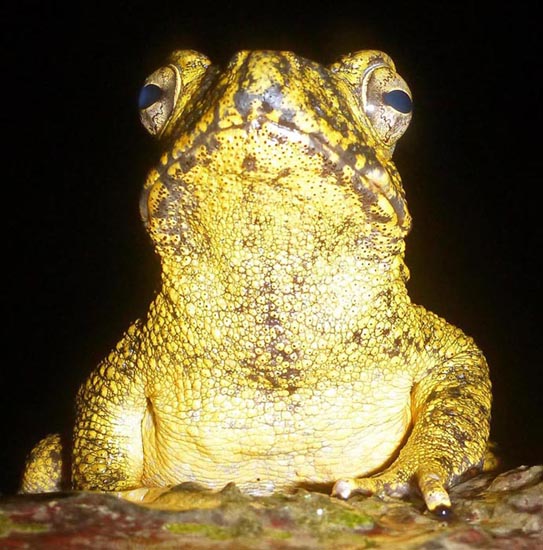 'Giant River Toad', (Our Jungle Home Lodge, Khao Sok, Thailand).
'Giant River Toad', (Our Jungle Home Lodge, Khao Sok, Thailand).One of the biggest groups of reptiles in the Asian rainforest are the 'dragons' of the family Agamidae.
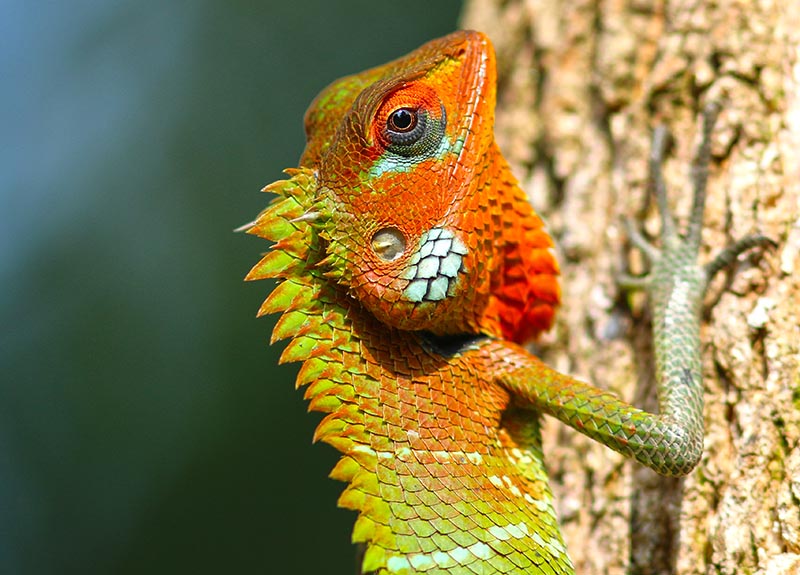 'Common Green Forest Lizard' (Kithugala, Sri Lanaka).
'Common Green Forest Lizard' (Kithugala, Sri Lanaka).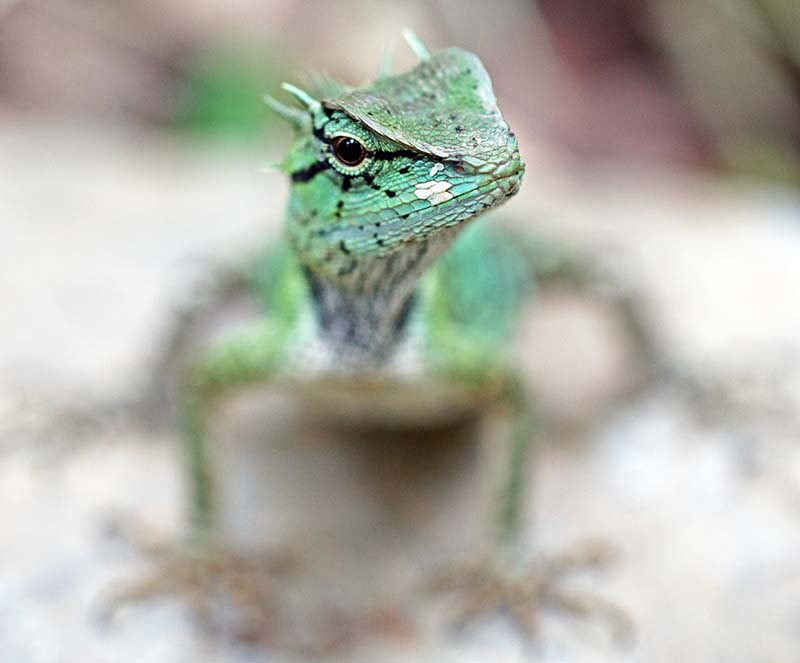 'Emma Gray's Forest/Crested Lizard' (Pala-U waterfall, Thailand).
'Emma Gray's Forest/Crested Lizard' (Pala-U waterfall, Thailand).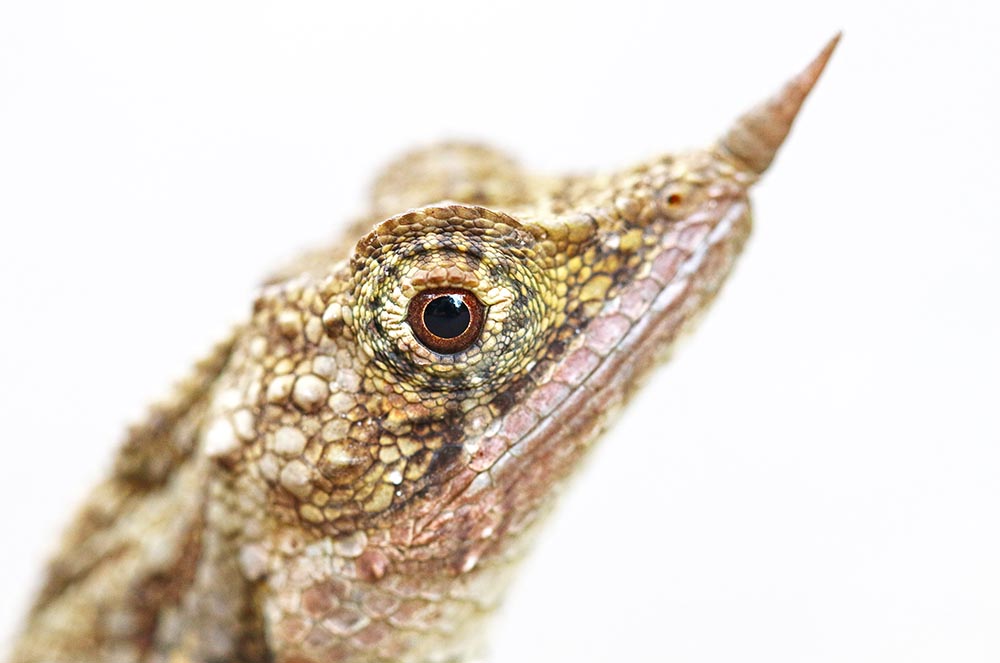 'Rhino Horned Lizard' (Horton Plains, Sri Lanka).
'Rhino Horned Lizard' (Horton Plains, Sri Lanka).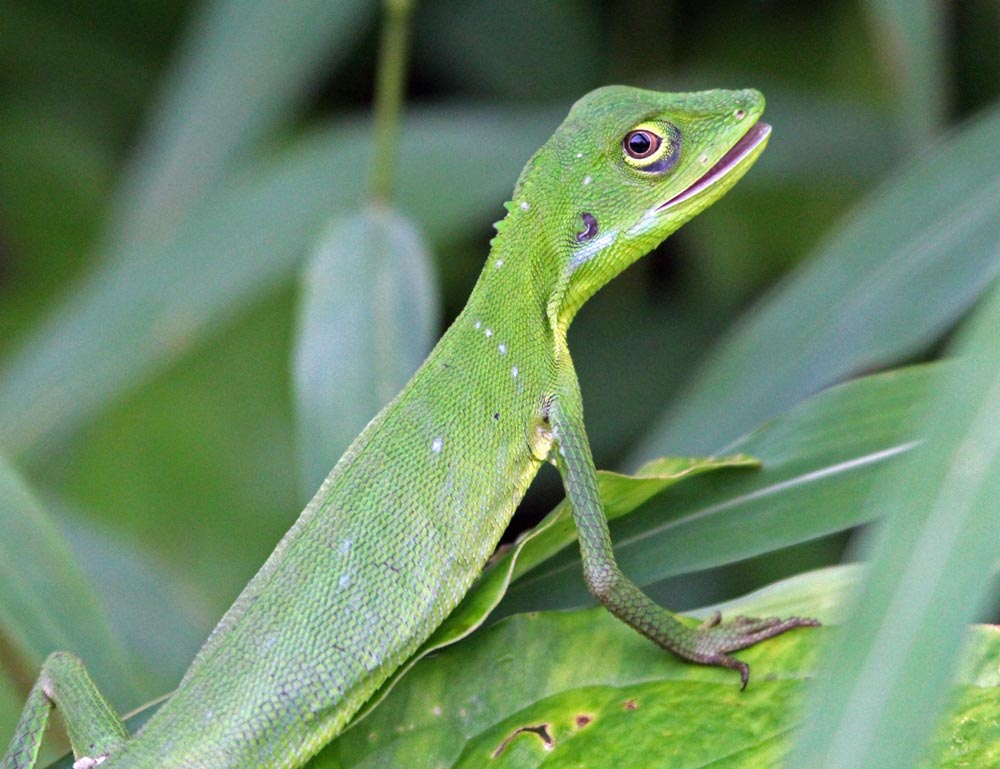 'Green Crested Lizard' (Khao Sok National Park, Thailand).
'Green Crested Lizard' (Khao Sok National Park, Thailand).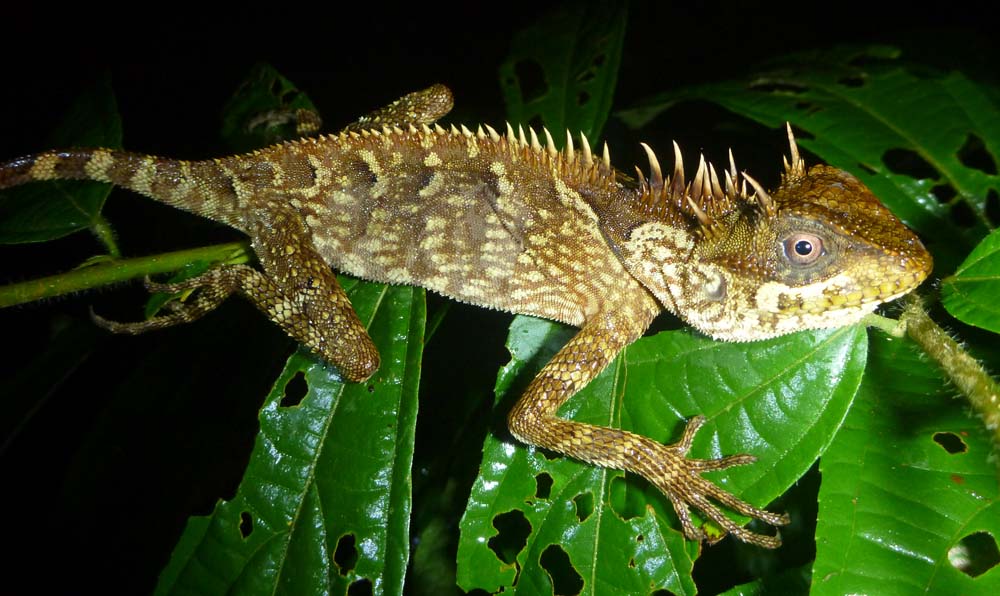 'Mountain Horned Lizard' (Khao Sok National Park, Thailand).
'Mountain Horned Lizard' (Khao Sok National Park, Thailand).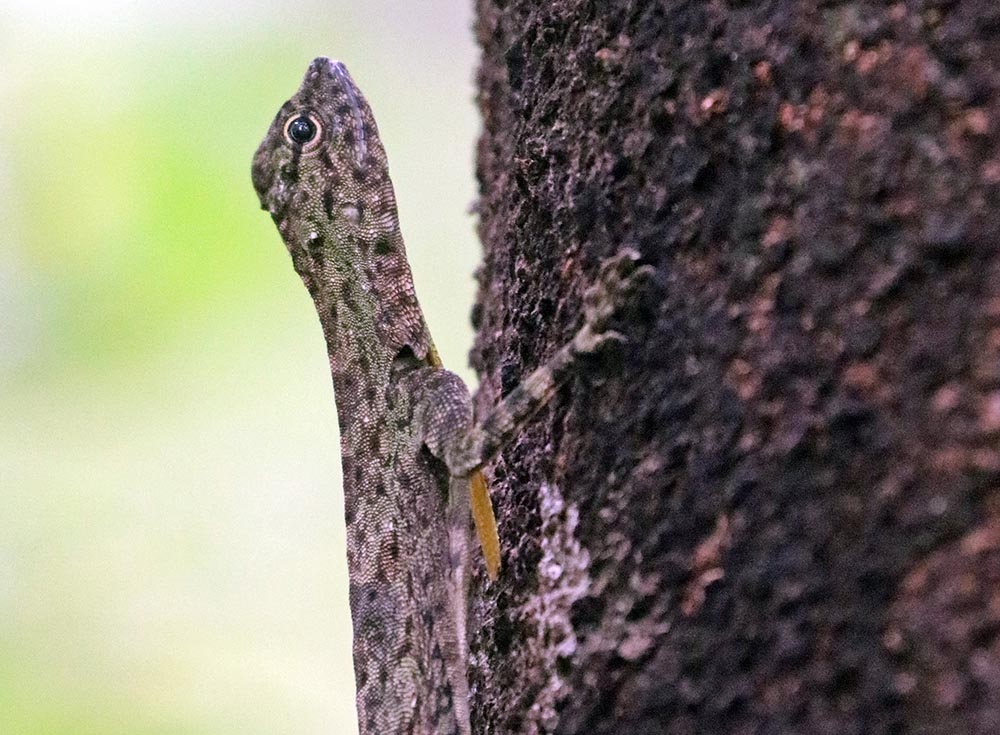 'Flying Lizard' (Jahoo Camp, Cambodia).
'Flying Lizard' (Jahoo Camp, Cambodia).The pigeons and doves of the family Columbidae are found all over the world, but there is a centre of diversity in the forests of tropical Asia.
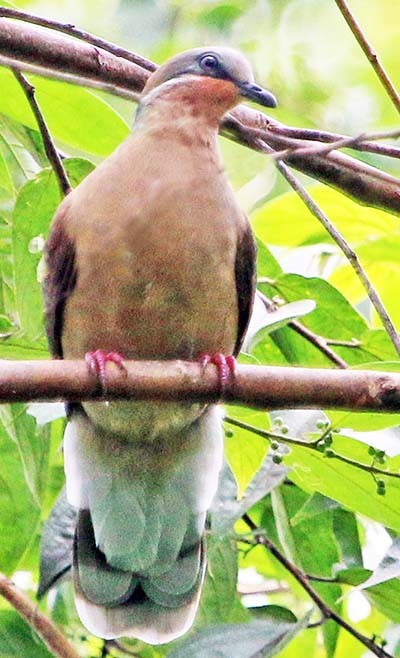 'White-eared Brown Dove' (Subic Bay, Philippines).
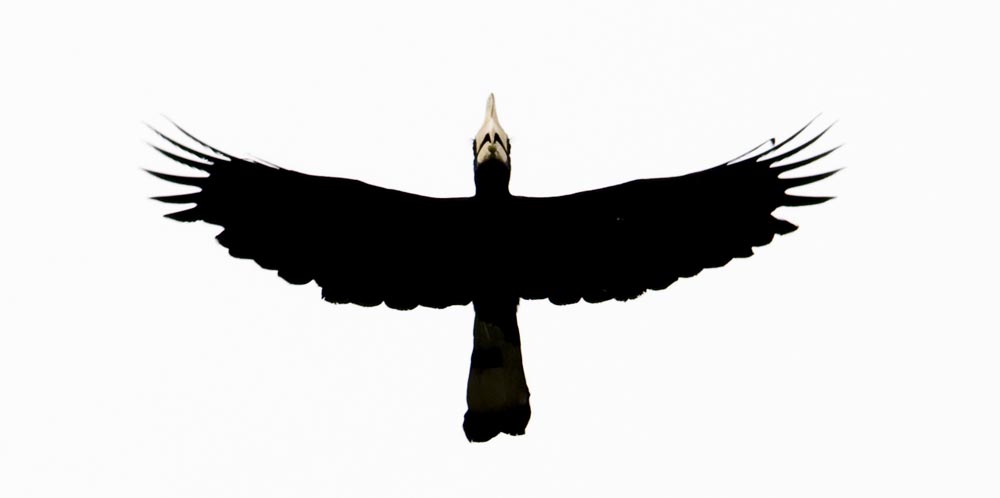
'White-eared Brown Dove' (Subic Bay, Philippines).Hornbills are large birds, and the swooshing of the wings of some species sounds like an approaching steam train!

Pitta are colourful birds of the rainforest floor. They are usually shy and sought after by birdwatchers. They are found throughout the tropical forests of the Old World, including tropical Asia.
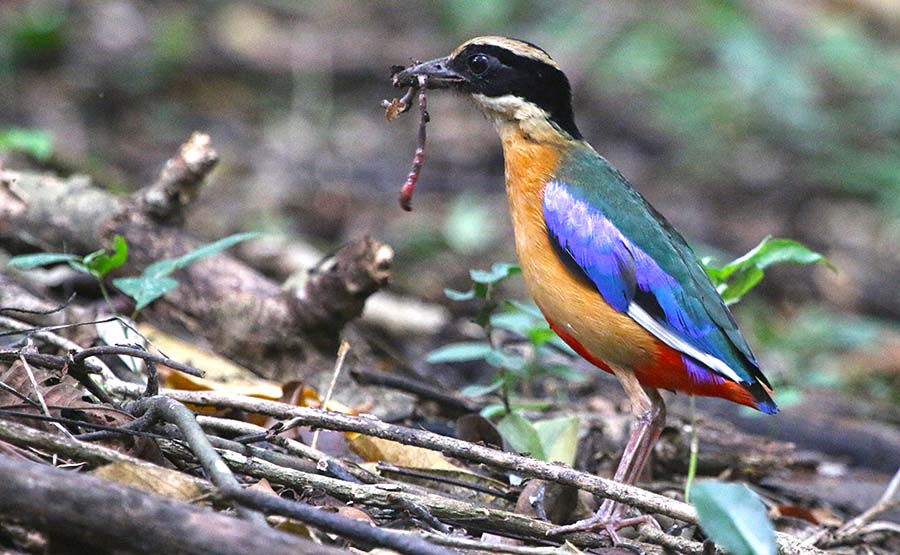 'Blue-winged Pitta' (Thailand).
'Blue-winged Pitta' (Thailand).If there is one group of birds that typifies the Asian rainforest, it is the Bulbuls. Although in Asia they are common in open areas, in any one area of rainforest, they are often the most commonly seen birds. Many species have yellow colours in their plumage.
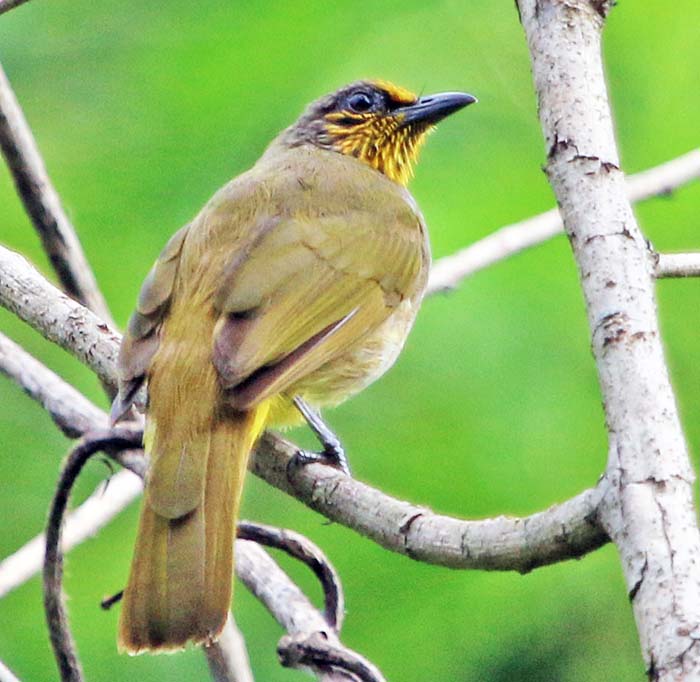 'Streak/Stripe-throated Bulbul' (Kaeng Krachan National Park, Thailand).
'Streak/Stripe-throated Bulbul' (Kaeng Krachan National Park, Thailand).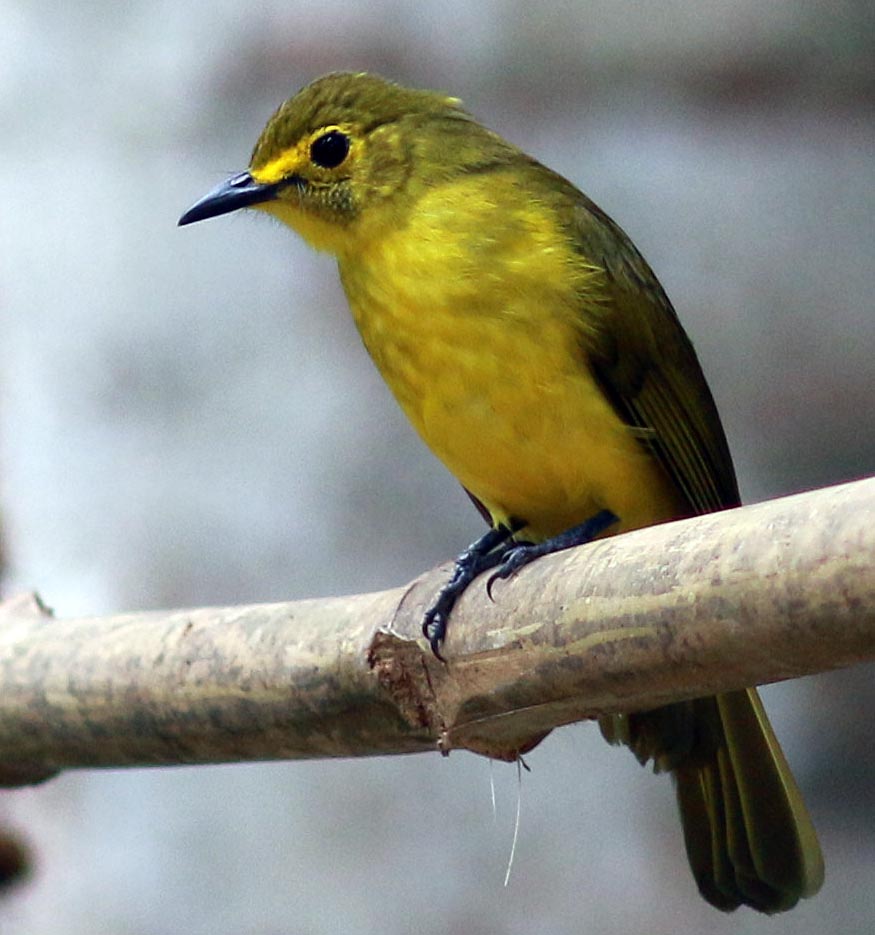 'Yellow-browed Bulbul' (Kelani, Sri Lanka).
'Yellow-browed Bulbul' (Kelani, Sri Lanka).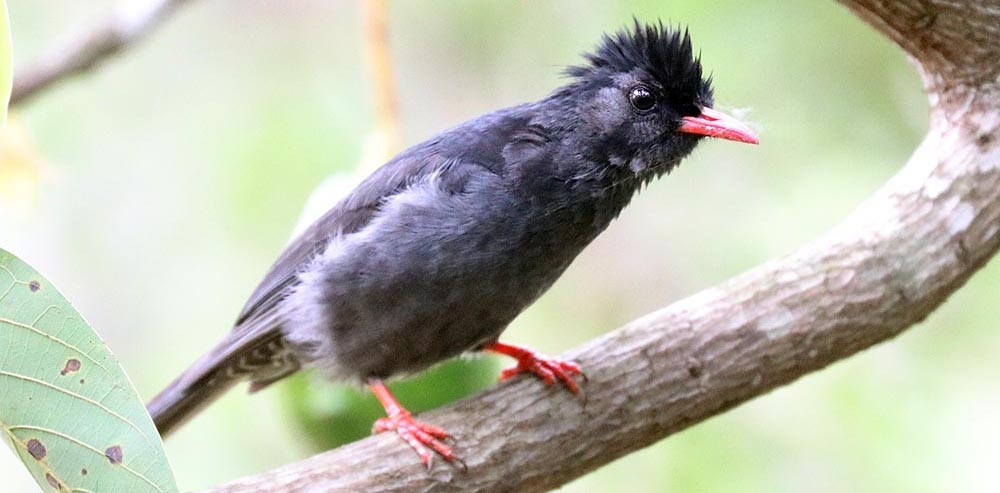 'Asian/Himalayan Black Bulbul', (Nature Lodge, Senmonorom, Cambodia).
'Asian/Himalayan Black Bulbul', (Nature Lodge, Senmonorom, Cambodia).One of the most sought after groups of birds are the 'Babblers'. This name covers various related but very different babblers, including Scimitar Babblers, Tit-Babblers, Ground Babbler and Laughing Thrush. Many of the species are also found in higher altitude temperate forests of Asia.
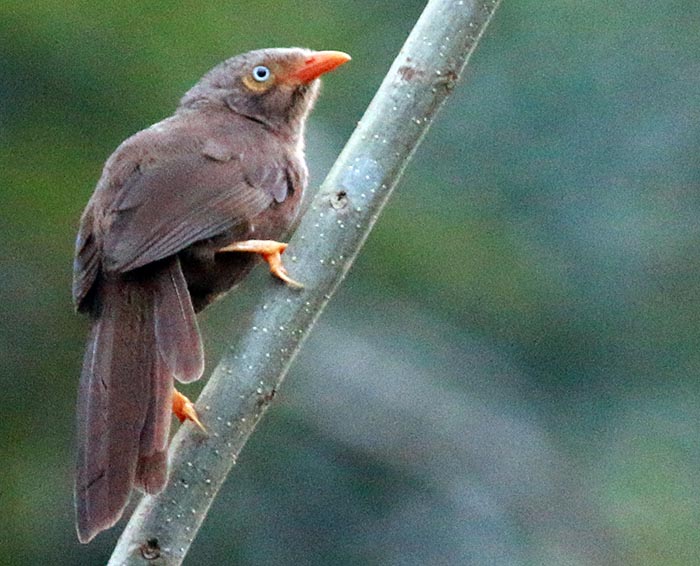 'Orange-billed Babbler', 'Sri Lankan Babbler', (Kithugala, Sri Lanka).
'Orange-billed Babbler', 'Sri Lankan Babbler', (Kithugala, Sri Lanka).The flowerpeckers of the family Dicaeidae include a range of smaller colourful birds found in the tropical Asian forest.
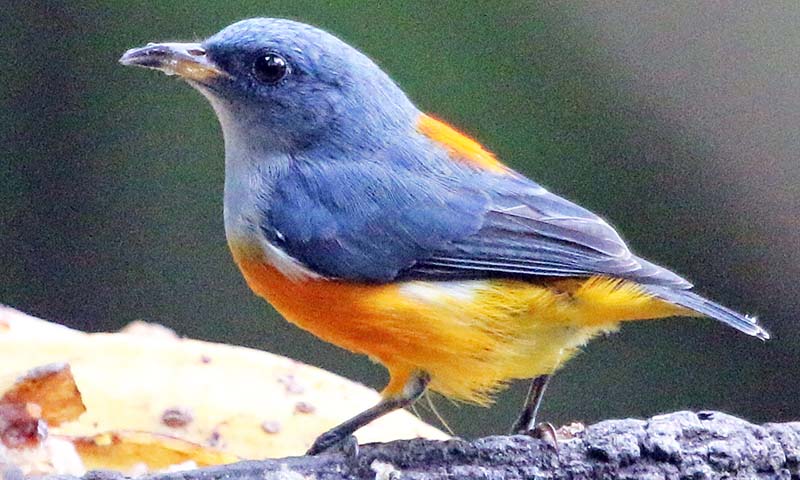 'Orange-bellied Flowerpecker' (Baak Man, Thailand).
'Orange-bellied Flowerpecker' (Baak Man, Thailand).The family Nectariniidae includes the 'Sunbirds'. Found throughout the old world tropics of Africa, Asia and Australasia, the group includes many colourful species in the Asian rainforest. Sunbirds are one of the most beautiful groups of birds in the world (and I think my own favourite). They have evolved to feed mainly on nectar from flowers, using their long curved bills. The rainforests of tropical Asia, particularly the higher altitudes, are one of the best places in the world to appreciate their diversity. Some species are also quite common on the forest edge and in gardens throughout tropical Asia, and can thus be easily seen and photographed.
Spiderhunters are a distinct group of larger sunbirds. They feed on nectar from long-tubed flowers with their long strong bill, but have also been recorded as nectar thieves, piercing the side of the flower. As suggested by their common name, they also hunt spiders, plucking them from the web while they hover.
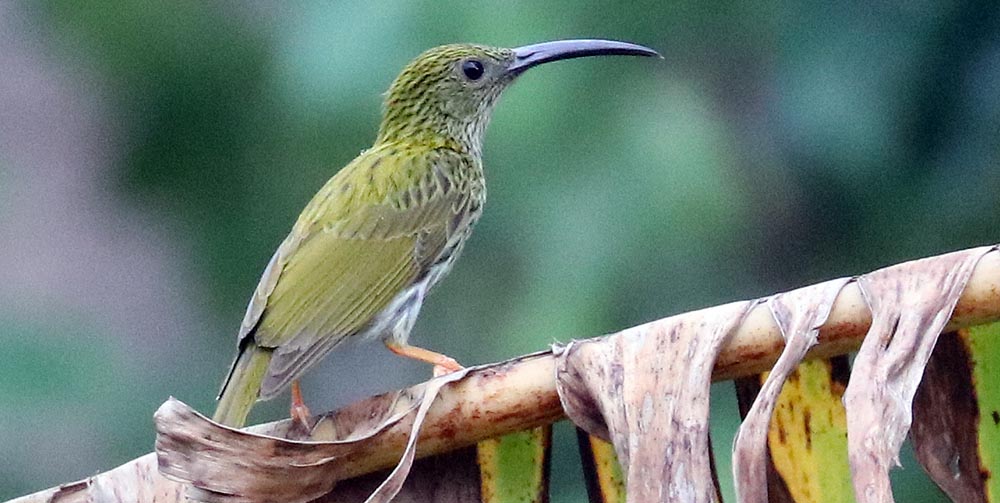 'Streaked Spiderhunter' (Seima, Cambodia).
'Streaked Spiderhunter' (Seima, Cambodia).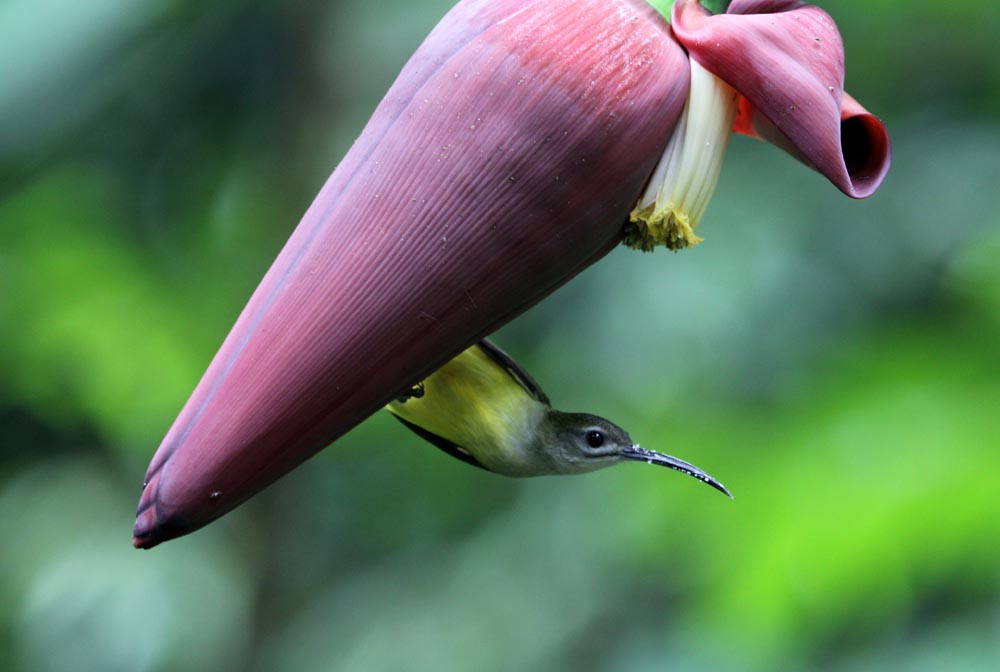 'Little Spiderhunter' (Our Jungle House, Thailand).
'Little Spiderhunter' (Our Jungle House, Thailand).There is one species of living elephant in Asia, the largest land mammal in this ecosystem...
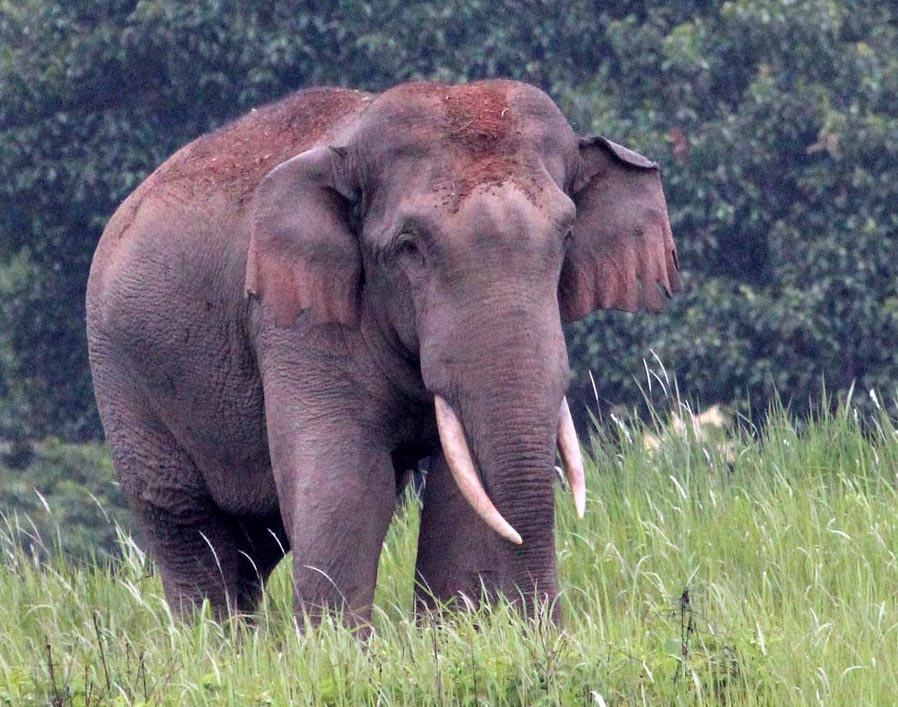

There are various hoofed animals in the Asian rainforest...
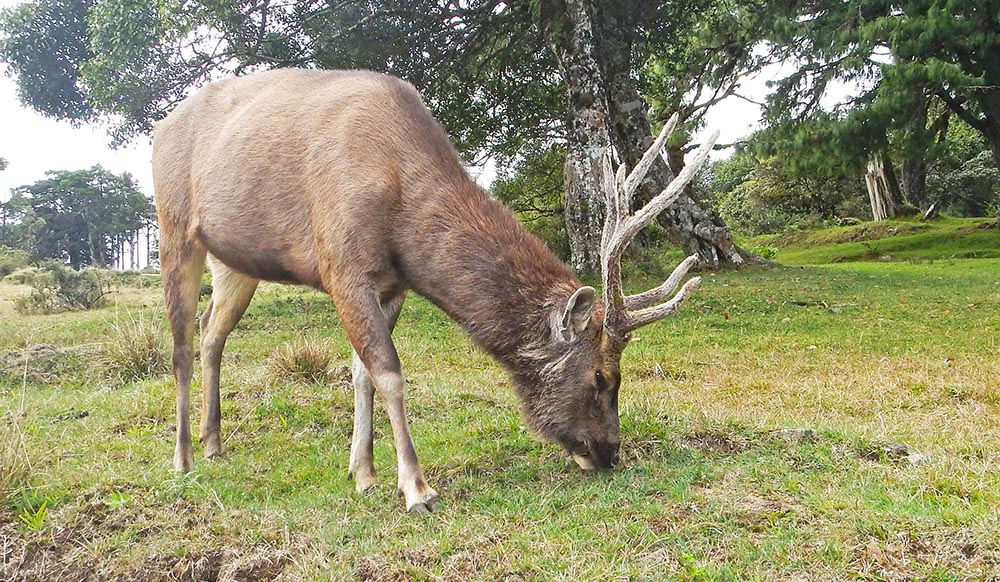 'Sambar' (Horton Plains, Sri Lanka).
'Sambar' (Horton Plains, Sri Lanka).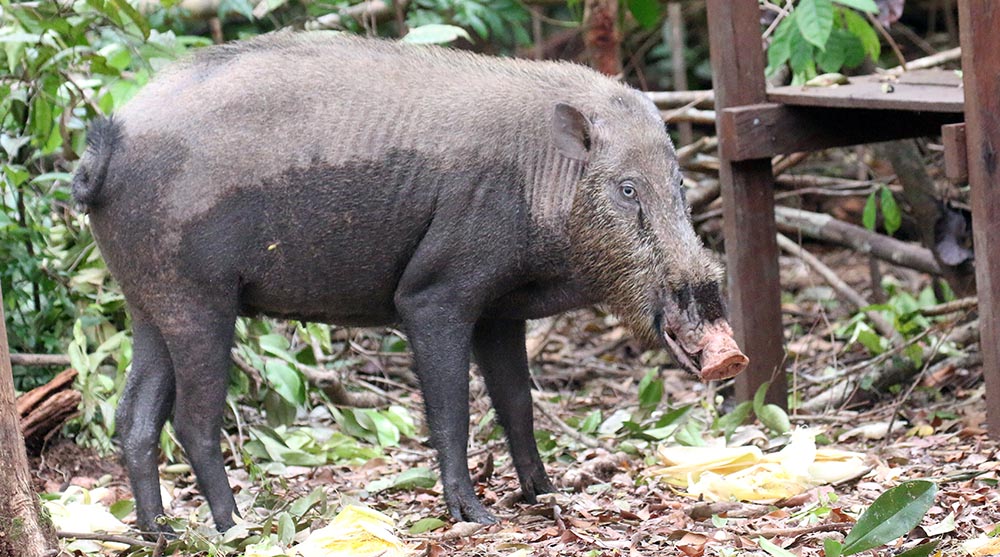 'Bearded Pig'(Tanjung Puting National Park, Borneo, Indonesia).
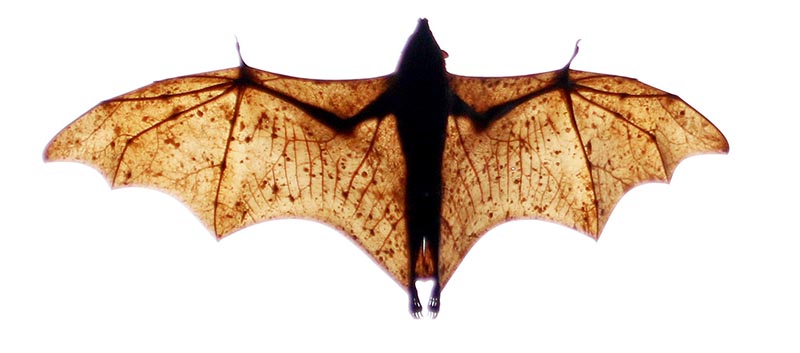
'Bearded Pig'(Tanjung Puting National Park, Borneo, Indonesia).After rodents, bats are the next largest group of mammals, and it is no different in the rainforests of tropical Asia. Here you can find tiny insect-eating bats, to giant fruit-eating 'Flying Fox'.
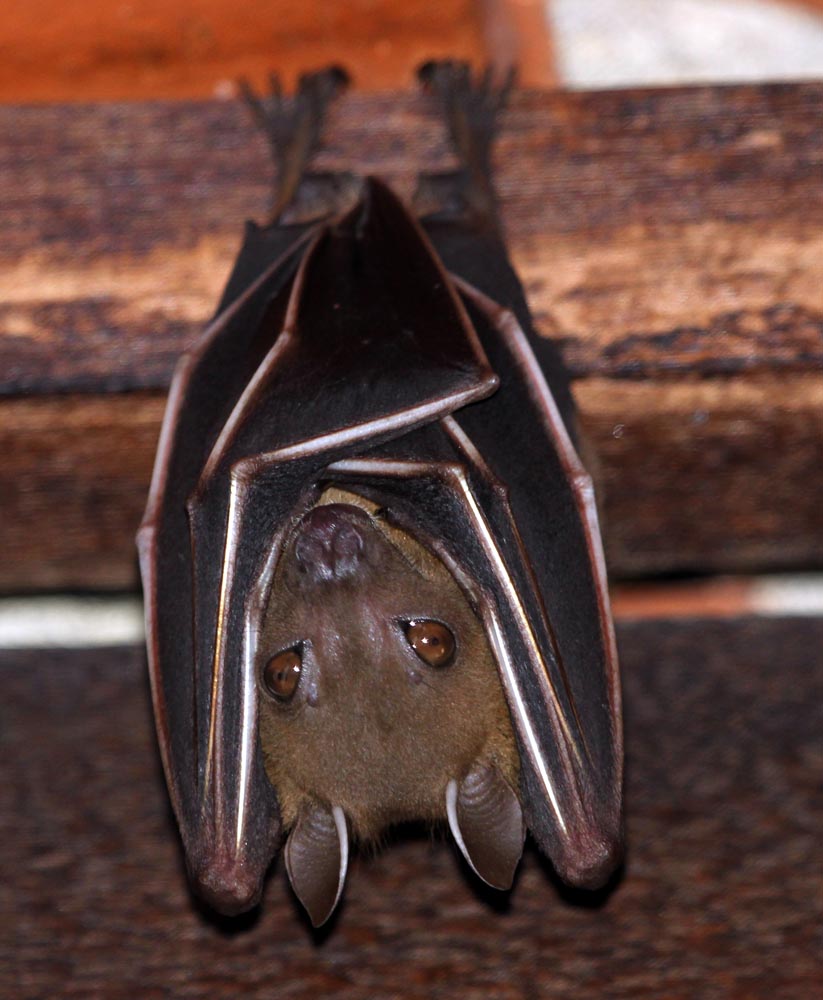

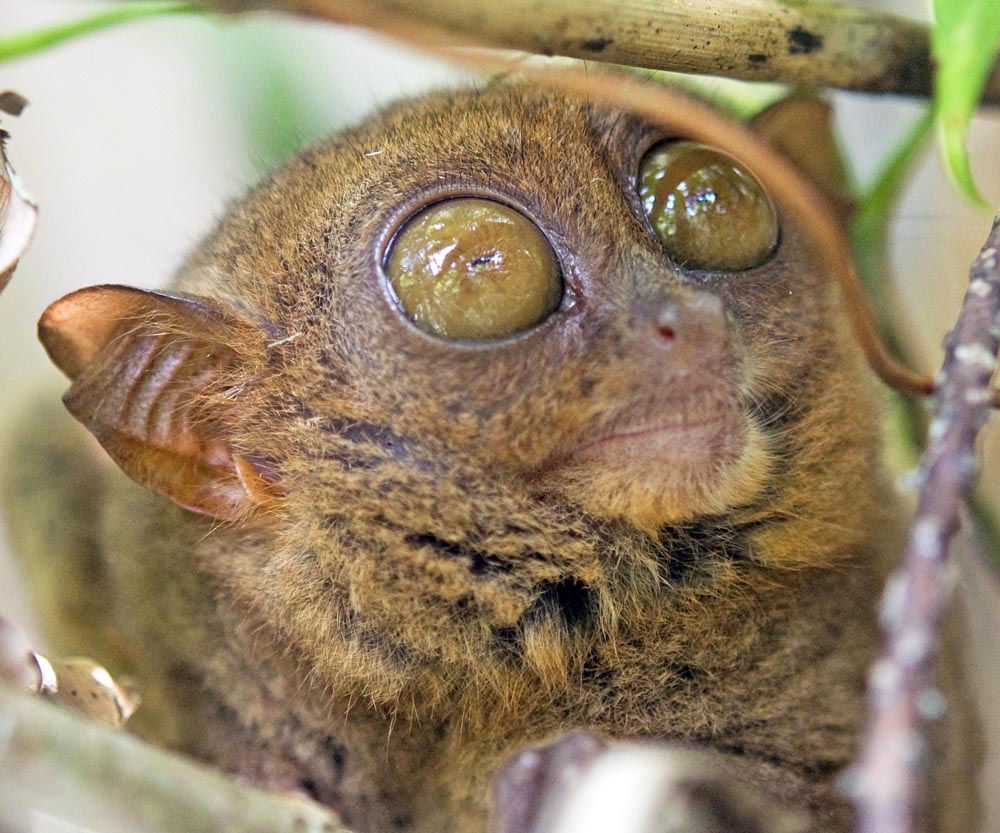
The smallest primates in the tropical Asian rainforest are the cute big-headed, big-eyed Tarsier. There are a number of species: below is Carlito syrichta, 'Philippine Tarsier'. Found in the south-eastern Philippines.

The Old World monkeys of the family Cercopithecidae are found across Africa and Asia. The Macaques are the most commonly seen group.
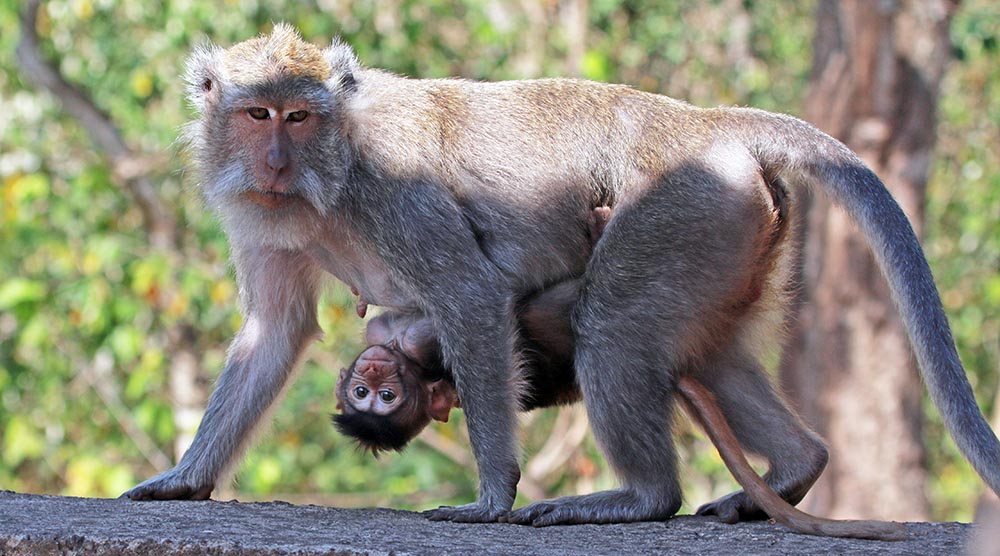 Macaca fascicularis, 'Long-tailed Macaque' mother and young.
Macaca fascicularis, 'Long-tailed Macaque' mother and young.The Langurs and Leaf Monkeys are the most diverse group of primates in the tropical Asian forests.
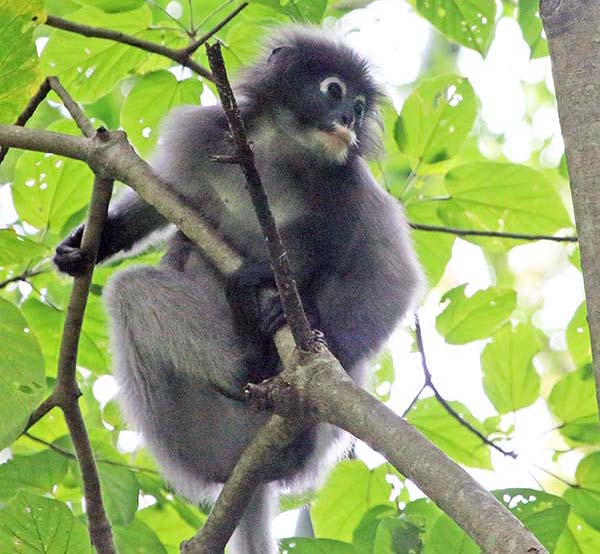 , 'Spectacled/Dusky Leaf Monkey' (Pala-U Waterfall, Thailand).
, 'Spectacled/Dusky Leaf Monkey' (Pala-U Waterfall, Thailand).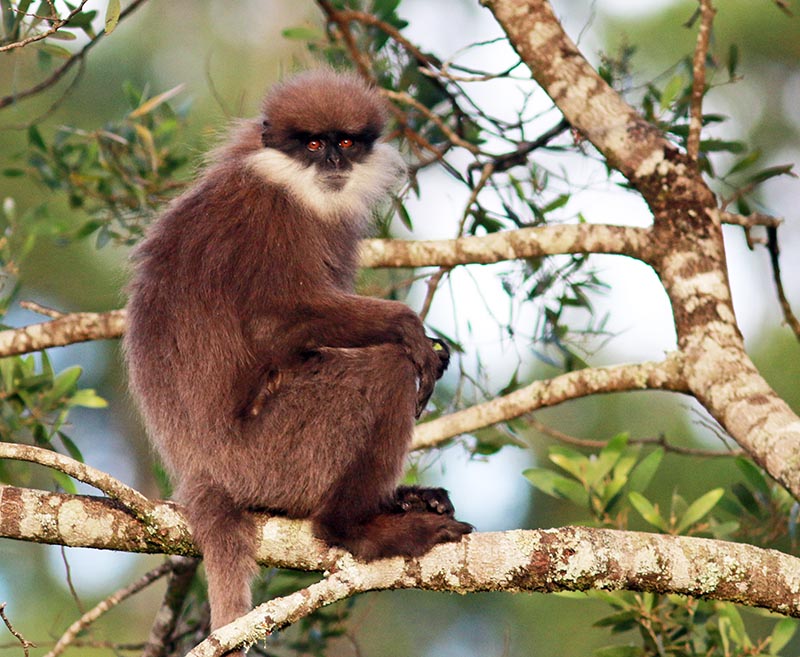 'Purple-faced Langur/Leaf Monkey', (Horton Plains, Sri Lanka)
'Purple-faced Langur/Leaf Monkey', (Horton Plains, Sri Lanka)There are some more unusual groups, such as the 'Douc' of the genus Pygathrix.
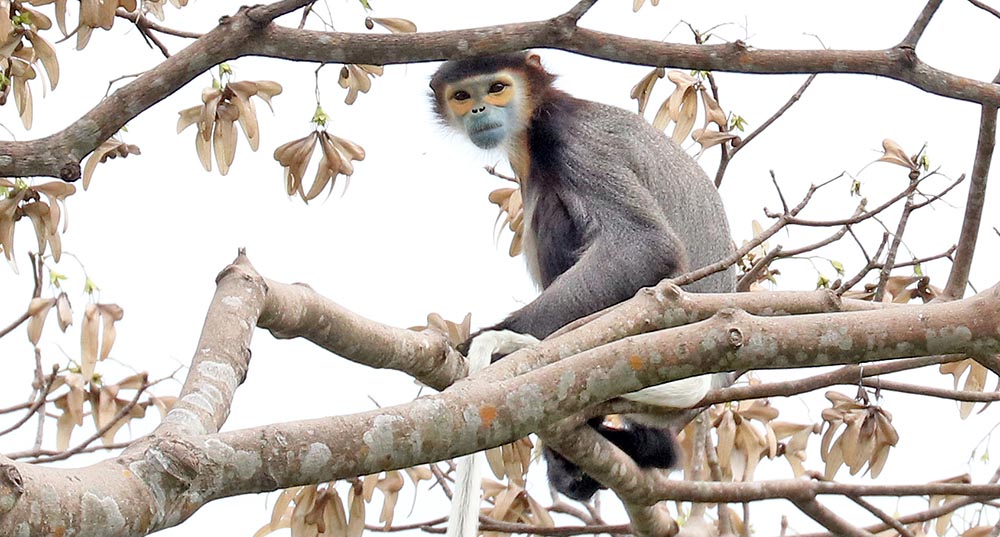 'Black-shanked Douc', (Keosemia, Cambodia)
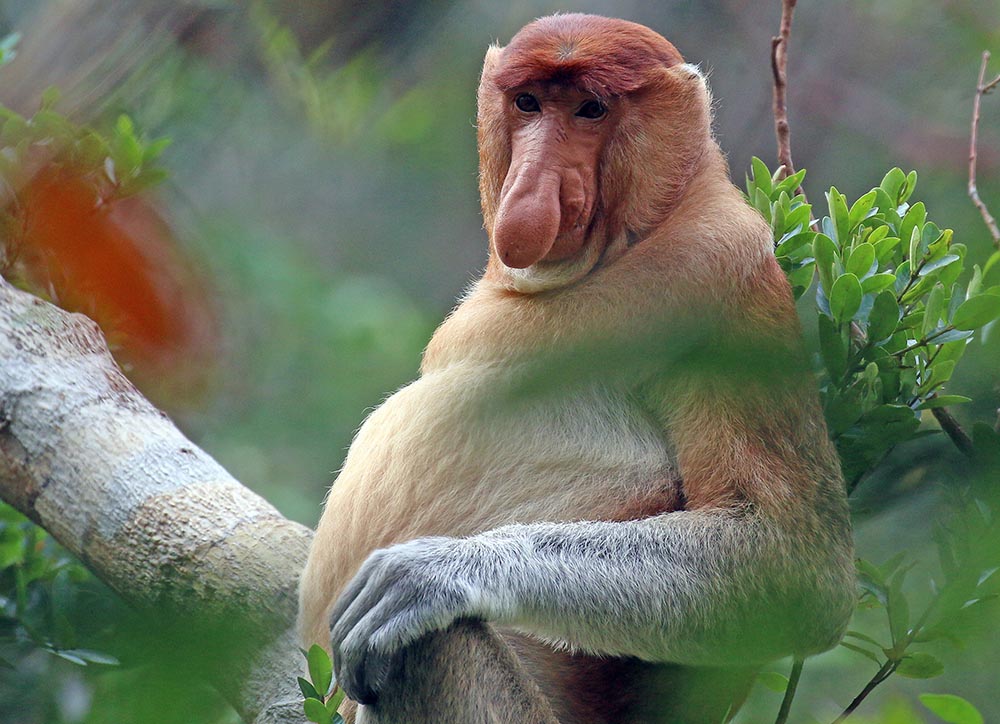
'Black-shanked Douc', (Keosemia, Cambodia)And the most famous unusual monkey of Asia, the 'Proboscis Monkey', is endemic to the rainforests and swamp forests of Borneo.

South-east Asia has the highest diversity of Apes in the world; those primates with no tails. The largest group are the gibbons. They have distinctively long arms, which they use to swing through the canopy in a movement called brachiation.
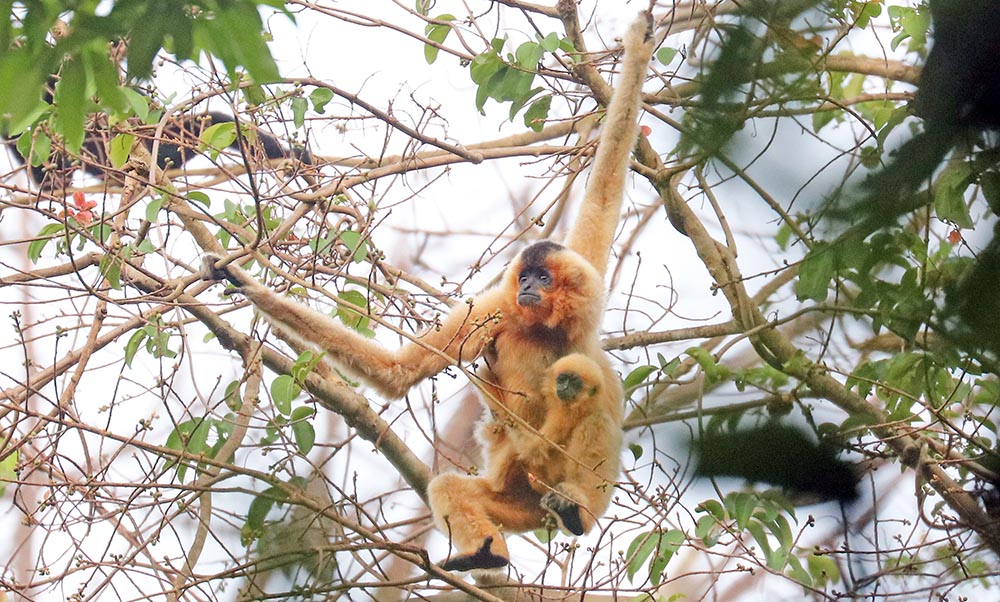 'Yellow-cheeked Crested Gibbon’, (Jahoo, Cambodia)
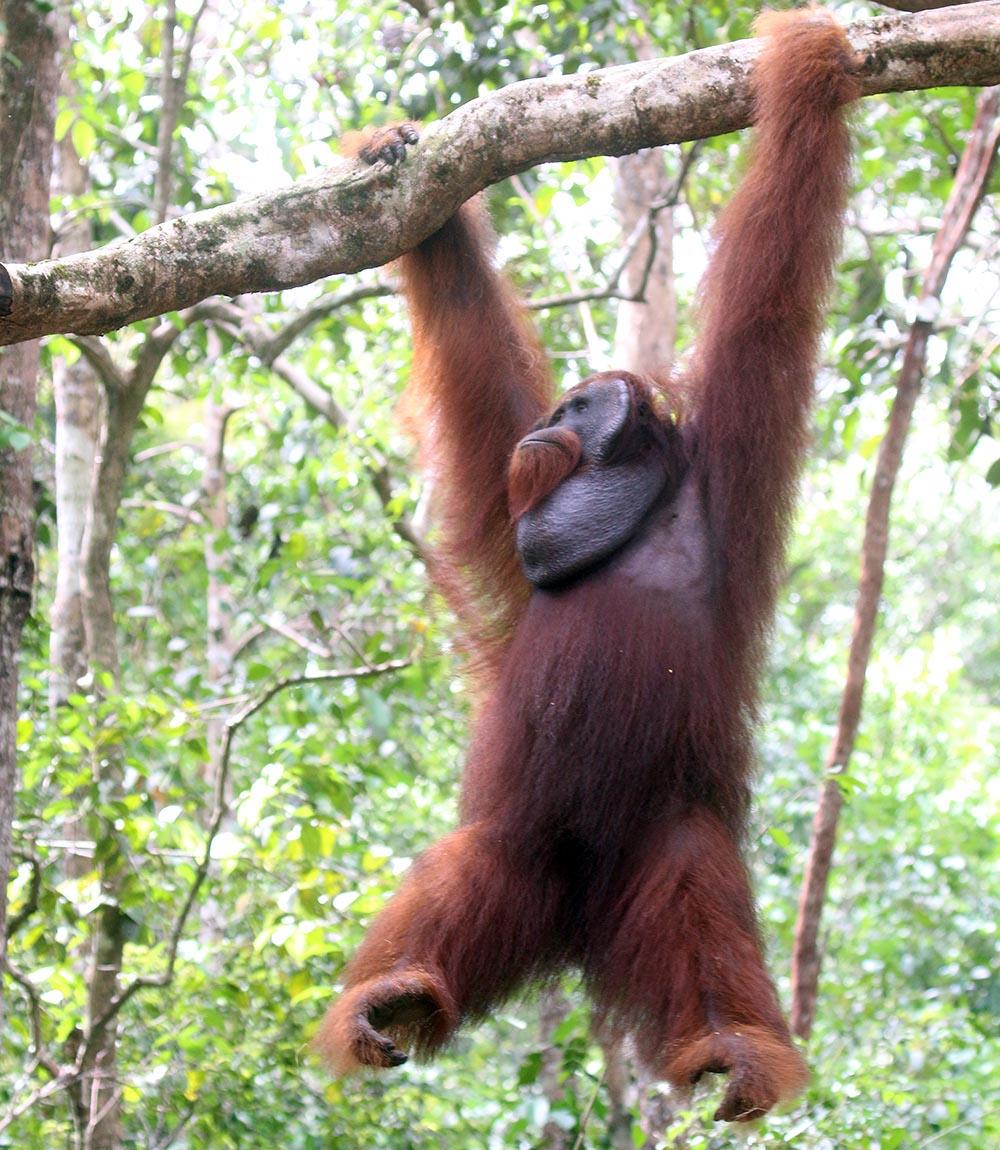
'Yellow-cheeked Crested Gibbon’, (Jahoo, Cambodia)And there of course the 'greater apes', such as the Orang-utans. They are the largest of arboreal animals. They generally don't leap or swing through the treetops; their technique is to grab a branch and pull it over, and then climb onto it. Sometimes they make the branch they are sitting in swing back and forth to get closer to their next handhold.

The squirrels of the family Sciuridae are common and diverse in the trees of the tropical Asian forests.
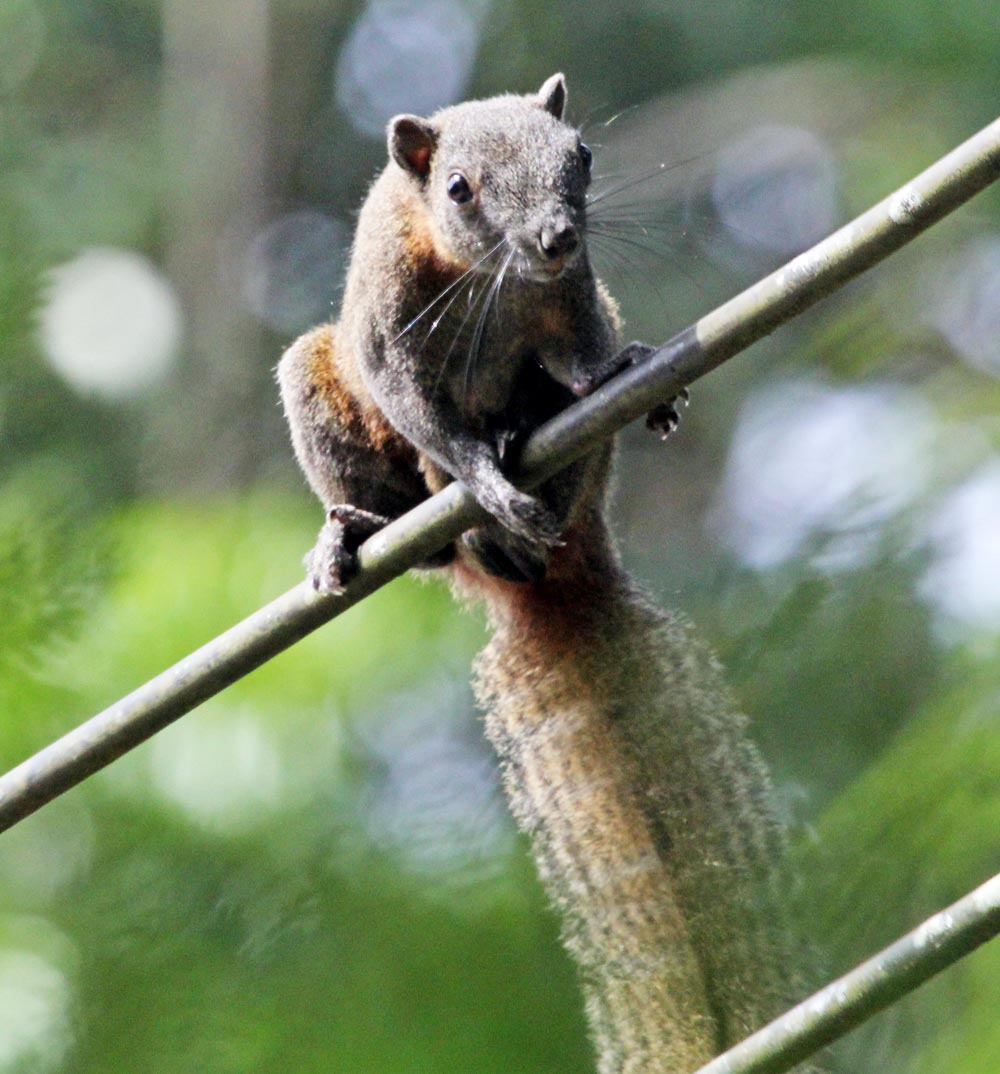 'Pallas's Squirrel', (Khao Sok National Park, Thailand)
'Pallas's Squirrel', (Khao Sok National Park, Thailand)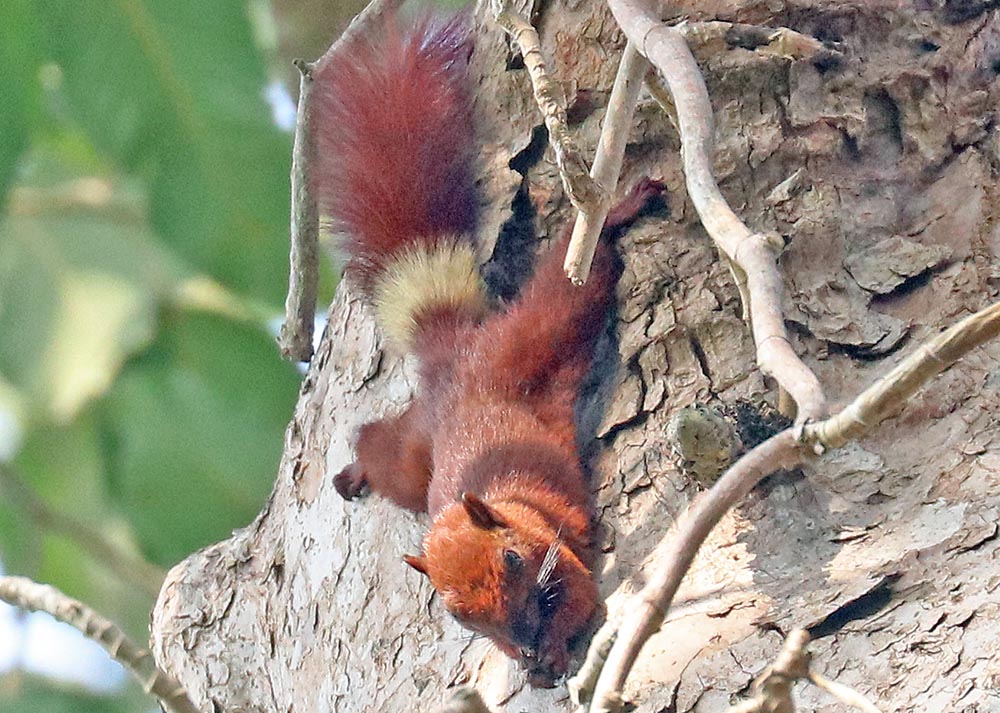 The local variation of 'Variable Squirrel', Callosciurus finlaysonii annellatus (Angkor Wat, Cambodia)
The local variation of 'Variable Squirrel', Callosciurus finlaysonii annellatus (Angkor Wat, Cambodia)They include the small striped squirrels, and the Giant Squirrels of the genus Ratufa.
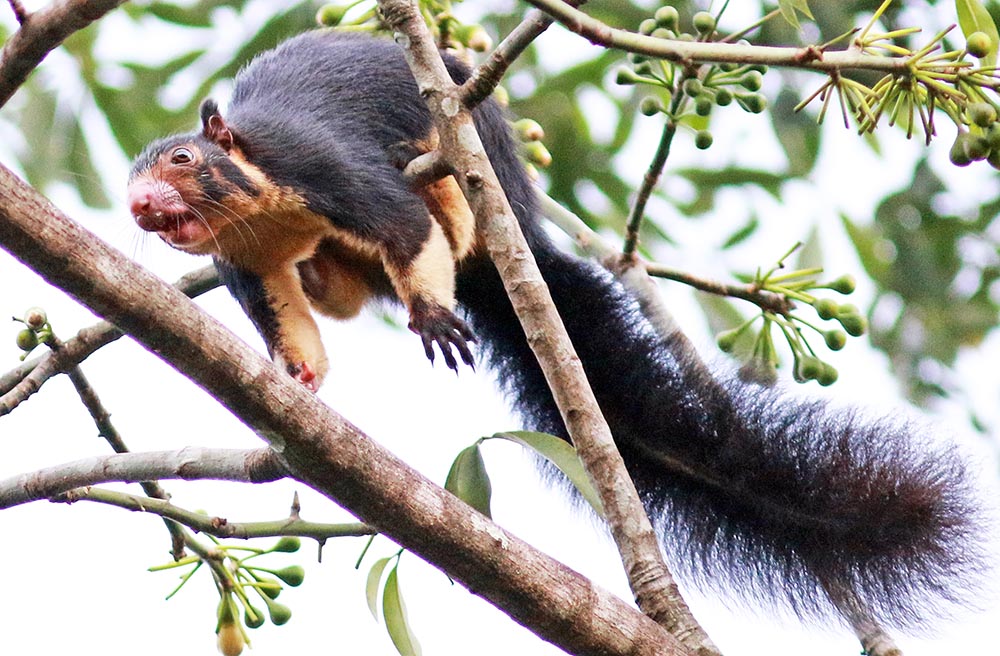 'Grizzled Giant Squirrel', (Kithugala, Sri Lanka)
'Grizzled Giant Squirrel', (Kithugala, Sri Lanka)Places to experience the Asian tropical rainforest
There are many lodges and nationals parks to see the lowland tropical rainforest of Asia.
In Sri Lanka, there is Kelani Forest Reserve, Kithugala, and Sinharaja Reserve.
In Cambodia there is: Angkor Wat, Keo-Seima Reserve, Nature Lodge at Senmonorom. In Thailand there is: Baan Maka Nature Lodge and Samarn Bird Camp which are near Kaeng Krachan National Park and Pala-U Waterfall, Thailand. There is also: Doi Inthanon National Park, Our Jungle House, great accommodation near Khao Sok National Park, There is also: Khao Yai National Park.
In the Philippines, there is: Subic Bay, Nuts Huts, which is on the island on Bohol.
In Malaysia there is: Taman Negara National Park. In Malaysian Borneo there is: Bako National Park, Kinabalu National Park HQ, Mesilau, Poring Hot Springs, and Sepilok. In Singapore, there is: Singapore Zoo. In Indonesia there is: Bali Barat National Park, Bukit Lawang & Gunung Leuser National Park, in Sumatra, Krakatoa, and Tanjung Puting National Park,Kalimantan in Borneo.



